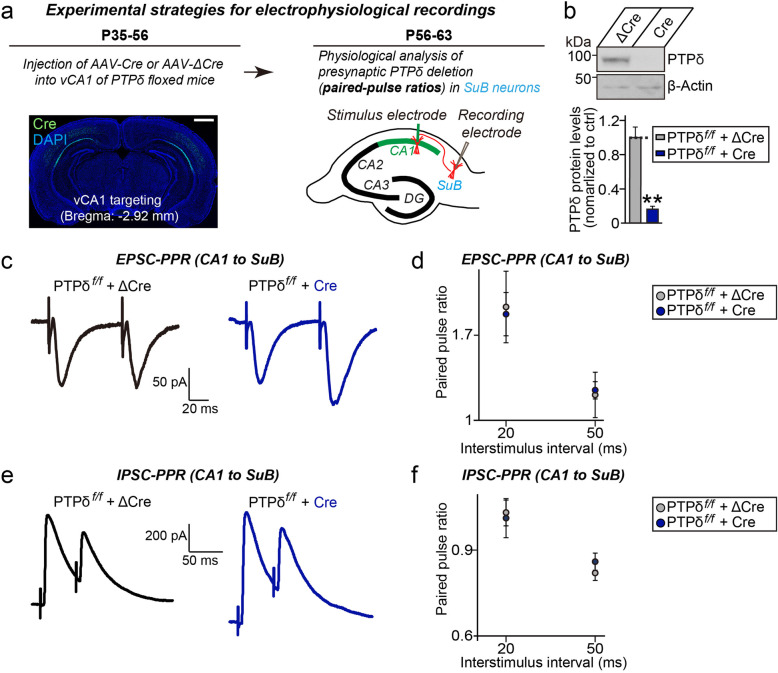
Fig. 4.
Presynaptic deletion of PTPδ in hippocampal CA1 neurons does not affect neurotransmitter release at excitatory or inhibitory synapses in postsynaptic subicular (SuB) pyramidal neurons. a, Experimental strategies for electrophysiological recordings in hippocampal SuB neurons innervated by PTPδ-deficient CA1 neurons. Representative coronal section showing EGFP expression after AAV-Cre injections into the ventral CA1 region of PTPδ floxed mice. Scale bar, 1 mm. b, Analysis of AAV-Cre expression in the hippocampal CA1 region of PTPδ-cKO mice. Representative immunoblot analyses (top) with PTPδ antibodies showing deletion of PTPδ protein in vivo. Infected mouse brain lysates were collected after stereotactic injection of AAV-Cre or AAV-ΔCre (Control) and immunoblotted with anti-PTPδ antibodies. Anti-β-actin antibodies were used as normalization controls. Quantitative analysis (bottom) of immunoblotting experiments. Data are means ± SEMs (n = 5 mice/group; **p < 0.01; Mann Whitney U-test). c, e, Representative traces of paired-pulse ratios (PPRs) of EPSCs (c) and IPSCs (e) in hippocampal CA1-SuB synapses at two different interstimulus intervals (20 and 50 ms). d, f, EPSC-PPRs (d) and IPSC-PPRs (f) in hippocampal CA1-SuB synapses as a function of the indicated interstimulus intervals. Data are means ± SEMs (n denotes the number of analyzed neurons; ΔCre [EPSC-PPR], n = 6; Cre [EPSC-PPR], n = 7; ΔCre [IPSC-PPR], n = 16; and Cre [IPSC-PPR], n = 12; two-tailed student’s t-test)