Figure 5.
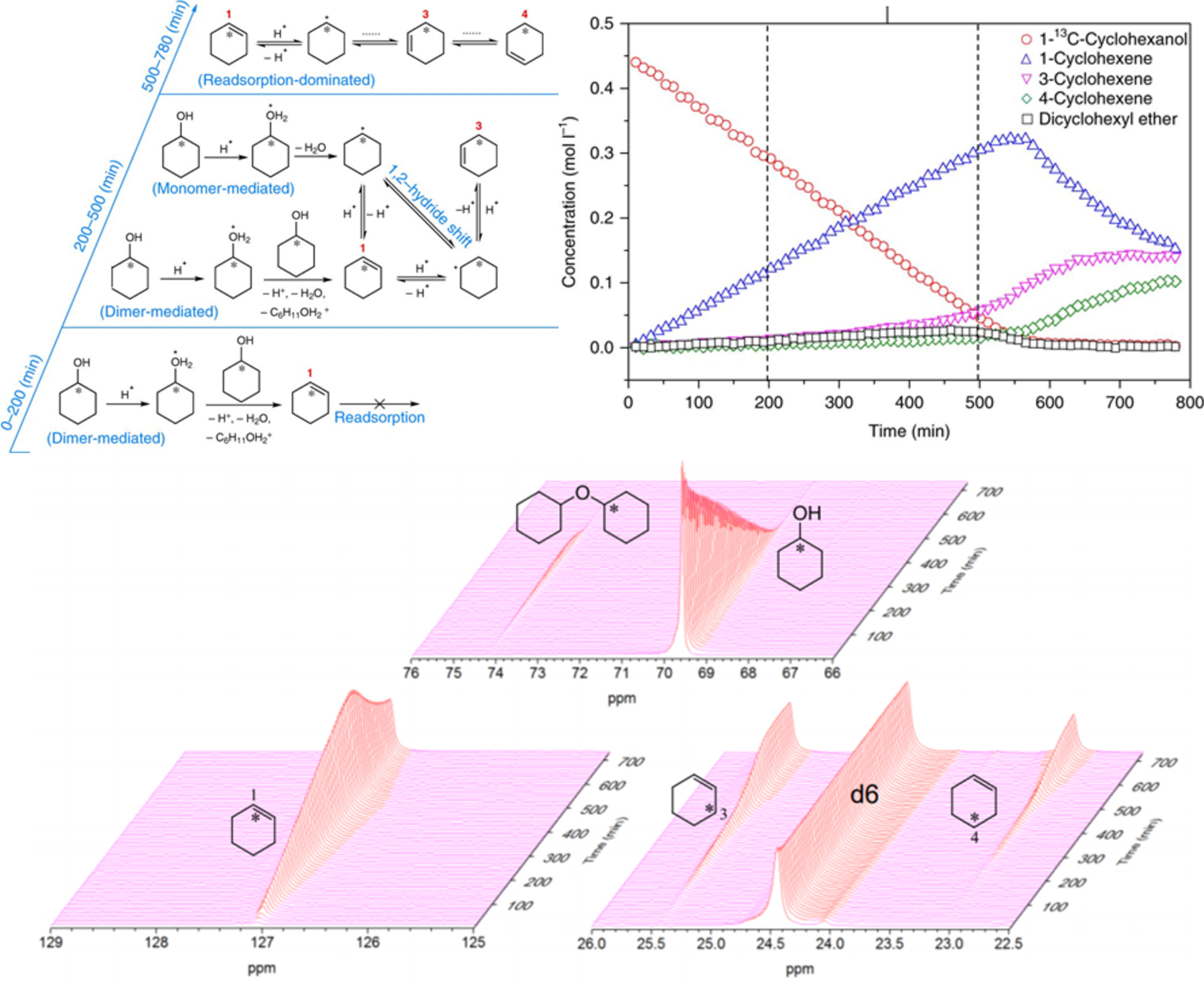
Reaction pathways proposed on the basis of in situ 13C NMR measurements of 1-13C-cyclohexanol dehydration on HBEA in decalin at 126 °C. Within 0–200 min, a significant fraction of the reaction occurs via elimination from alcohol dimer species (the monomer path not shown), while cyclohexene readsorption is severely hindered; within 200–500 min, olefin formation occurs via monomeric (increased contribution) and dimeric cyclohexanol (reduced contribution), and cyclohexene readsorption becomes less hindered with decreasing surface abundance of dimer species; within 500–780 min, cyclohexene readsorption becomes more pronounced after more than 70% of cyclohexanol is converted, and the distribution of labels becomes fully randomized at the end. The corresponding stacked plots for these 13C MAS NMR-derived concentration data are presented on the bottom. Adapted with permission from ref 42. Copyright 2018 Springer.
