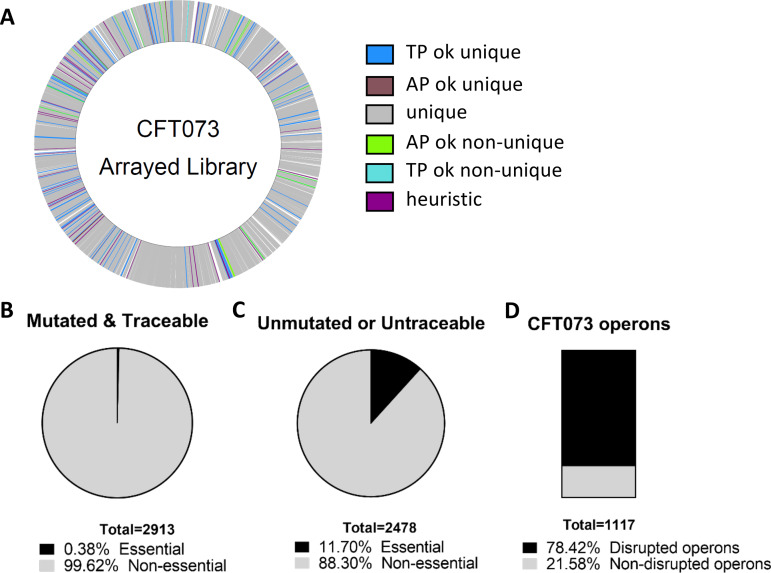
FIG 1.
Construction and identification of transposon mutants within the library. A total of 9,216 E. coli CFT073 mutants were generated and sequenced to identify the locations of transposon insertions. (A) The CFT073 genome is marked with each identified transposon insertion site. Unique, unique identification of the plate and well coordinates within the library; TPok_unique, unique identification of the plate coordinate and the most highly probable unique location for the well coordinate; TPok_nonunique, unique identification of the plate coordinate and multiple locations for the well coordinate; APok_unique, unique identification of the well coordinate and the most highly probable unique location for the plate coordinate; APok_nonunique, unique identification of the well coordinate and multiple locations for the plate coordinate; heuristic, the most highly probable unique location for the plate and well coordinates. (B) A total of 2,913 genes had a traceable transposon insertion; 99.9% of these were in nonessential genes. (C) Of the 2,478 nonmutated genes in the CFT073 genome, 290 are annotated as essential. (D) There are 1,117 annotated operons in the CFT073 genome. Sequencing of the ordered library confidently identified transposon insertions in 876 unique operons.