FIG 5.
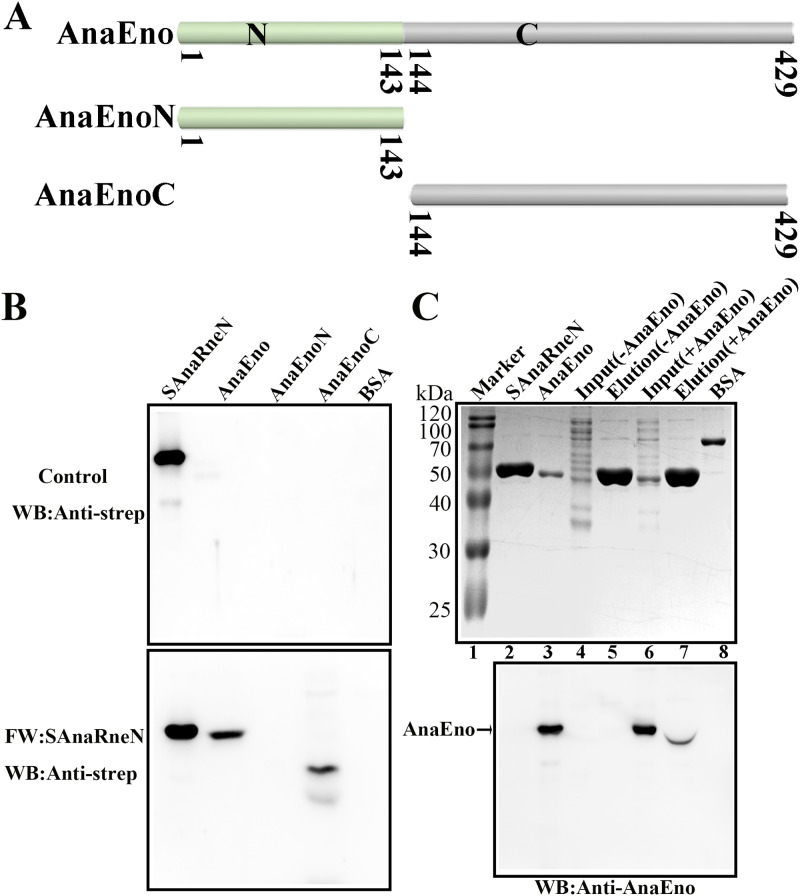
The C-terminal domain of AnaEno can interact with AnaRneN. (A) Schematic of AnaEno and its truncated derivatives based on the SMART analysis. SMART analysis is available as a Web resource (http://smart.embl.de) designed to identify and annotate protein domains and to analyze protein domain architectures (51). The numbers indicate the amino acid positions. (B) Far-Western blotting assay investigating the interaction between AnaEno and AnaRneN. One of the PVDF membranes was incubated with SAnaRneN (bottom). The other (top) was incubated with skim milk as a control. The final results were detected with the anti-strep antibody. SAnaRneN purified from E. coli was employed as a positive control, while BSA was employed as a negative control. Other proteins were purified with the C-terminal His tag. The amount of protein was 1 μg, with the exception that it was 20 ng for the positive control. (C) The pulldown assay detecting the interaction of AnaRneN and AnaEno. Cell lysates expressing AnaEno or not were applied to Strep-Tactin Sepharose with bound SAnaRneN and eluted with d-biotin. Eluted samples were loaded onto a 10% gel for SDS-PAGE (top) and were next subjected to WB with the anti-AnaEno antibody for detection (bottom). Marker lane (lane 1), Blue Plus II protein markers (TransGen) (14 to 120 kDa); lane 2, SAnaRneN (purified from E. coli) (positive control); lane 3, AnaEno (purified from E. coli) (positive control); lane 4 [Input (-AnaEno)], a cell lysate without AnaEno input; lane 5, [Elution (-AnaEno)], an elution sample after incubation with SAnaRneN and cell lysate as described for lane 4; lane 6 [Input (+AnaEno)], cell lysate expressing AnaEno input; lane 7 [Elution (+AnaEno)], an elution sample following incubation with SAnaRneN and cell lysate as described for lane 6; lane 8 (BSA), negative control. Results presented here are representative of three independent experiments.