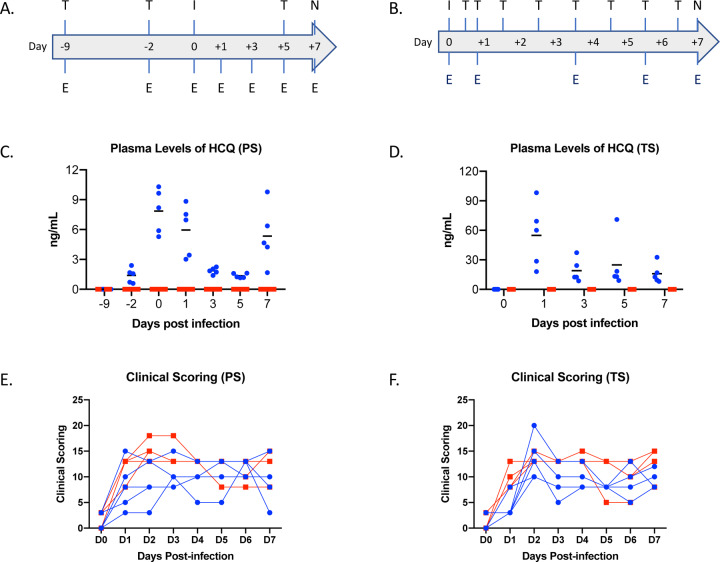
Figure 2: Rhesus macaque model – design, drug concentrations and clinical scoring.
Macaques were infected with SARS-CoV-2 by the combined intratracheal, intranasal, oral and ocular routes. Animals were treated by oral gavage with either vehicle (PBS) or HCQ (6.5mg/kg in PBS). Administration was either one time per week for the prophylaxis arm or starting 12 hours post-infection followed by treatment at 18, 36, 60, 86 and 108 hours post-infection for the treatment arm. Animals were scored for clinical disease twice daily and examinations were performed as indicated. (A and B) Study design. The schematic depicts infection (‘I’), HCQ or vehicle treatment (‘T’) and examinations (‘E’). (C and D) Plasma levels of HCQ. HCQ levels were determined in both the prophylaxis and treatment study arms. Measurements reflect pre-dose levels of HCQ at each timepoint (limit of quantification = 0.5 ng/mL). (E and F) Clinical scores. Clinical scoring was performed twice daily by observation of non-anesthetized animals. The morning score is graphed here. Multiple t tests performed on individual days found no significance difference between groups. Area under the curve analysis was performed on each individual animal in each study. This analysis found a significant difference (p=0.004) between groups in the therapeutic study only. Note: red squares, vehicle-treated animals; blue circles, HCQ-treated animals; PS, prophylaxis; TS, treatment.