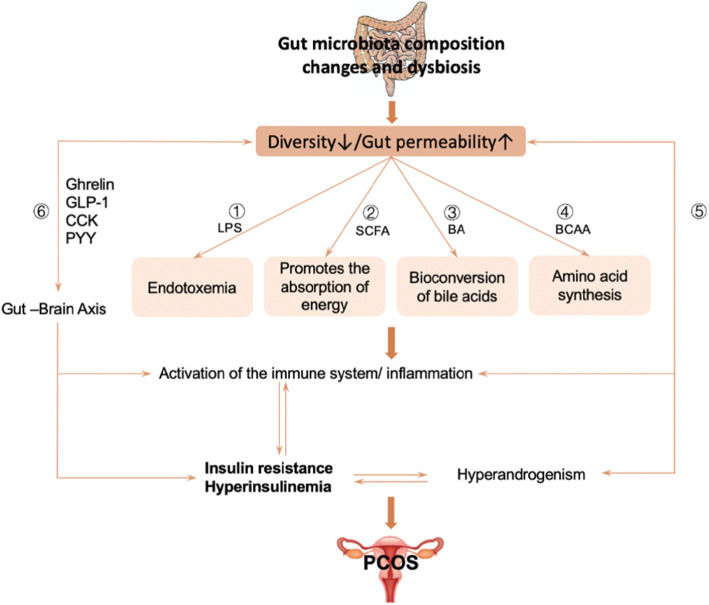
Fig. 2.
①Gut microbiota can cause IR by affecting lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and its receptor CD14(LPS-CD14; ②SCFAs protect intestinal barrier integrity and act on beta cells to promote insulin secretion, thus improving metabolism; ③Bile acids (BAs) are signaling molecules that regulate glucose metabolism and promote insulin sensitivity; ④The metabolic disorder of amino acids might aggravate IR by changing glucose metabolism or inducing inflammation;⑤A vicious cycle between hyperandrogenemia and IR in PCOS, thus promoting the occurrence and development of PCOS; ⑥Gut microbiota and its metabolites cause insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia by stimulating the secretion of gut-brain peptides and regulating inflammation pathway activation. LPS: lipopolysaccharide; SCFA: short-chain fatty acid; BCAA: branch-chain amino acid; BA: Bile acids