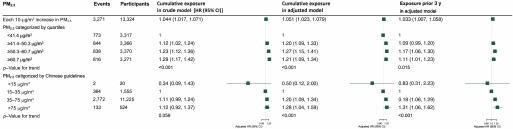
Figure 3.
The association of particulate matter with aerodynamic diameter () and poor cognitive function [Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) ] in competing risk models among Chinese older adults 65 years of age and older. Adjusted covariates include age (continuous), sex, residence, current marital status, living pattern, education (literacy status), smoking status, alcohol drinking status, regular exercise, diabetes, heart disease, hypertension, respiratory disease, disability in activities of daily living, gross domestic product (GDP), physicians per z persons at prefecture level. Note: CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio.