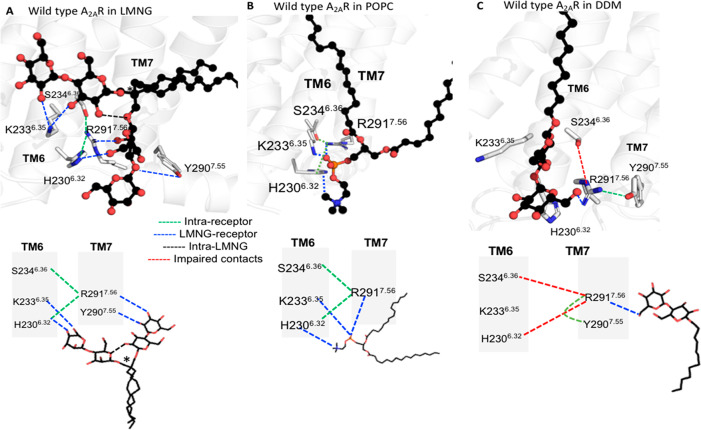
Figure 6.
Branched detergent LMNG forms bifurcated hydrogen bonds between TM helices and loops in WT-A2AR. WT-A2AR is shown in white cartoon representation, and the detergents and POPC are shown in ball-and-stick representation (oxygen atoms of the polar head groups shown as red spheres). The hydrogen bonds within the receptor are shown as green dotted lines, those between LMNG and the receptor as blue dotted lines, those within the LMNG molecule as black dotted lines, and those that are broken as red dotted lines. (A) Bifurcated hydrogen bonds formed by the two polar head groups of LMNG. The two-dimensional schemes of the hydrogen bond patterns are also shown (bottom). The quaternary carbon atom of LMNG is denoted with an asterisk. (B) Bifurcated hydrogen bonds formed by the POPC head group and WT-A2AR in the lipid bilayer. The two-dimensional (2D) scheme of the hydrogen bonds is also shown (bottom). (C) Hydrogen bonds between DDM and the receptor and the 2D scheme (bottom). The Ballesteros–Weinstein (BW) residue numbering scheme is shown as superscripts.