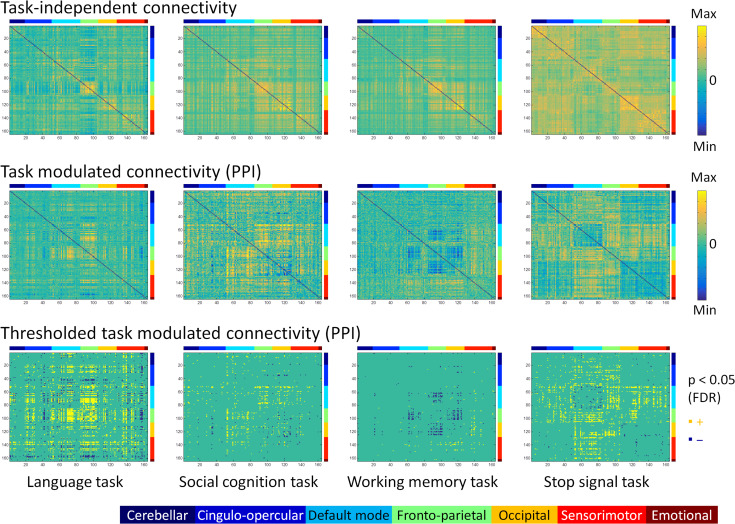
Figure 2.
Whole brain task-independent connectivity (top row) and task modulated connectivity (middle and bottom rows) matrices for the language, social cognition, working memory, and stop signal tasks across 164 regions of interest. The upper 2 rows showed unthresholded matrices. The displayed range for each matrix was adjusted for each matrix, and was assured to be positive and negative symmetrical. The bottom row showed thresholded matrices of task modulated connectivity at P < 0.05 of FDR (false discovery rate) correction. Yellow and blue elements in the matrices indicate increased and decreased connectivity between each task and its corresponding control conditions. The color bars on the top and right side of each matrix represent 7 functional brain modules: (1) cerebellar, (2) cingulo-opercular, (3) default mode, (4) frontoparietal, (5) occipital, (6), sensorimotor, and (7) emotional modules.