Figure 3. SMN pre-mRNA alternative splicing.
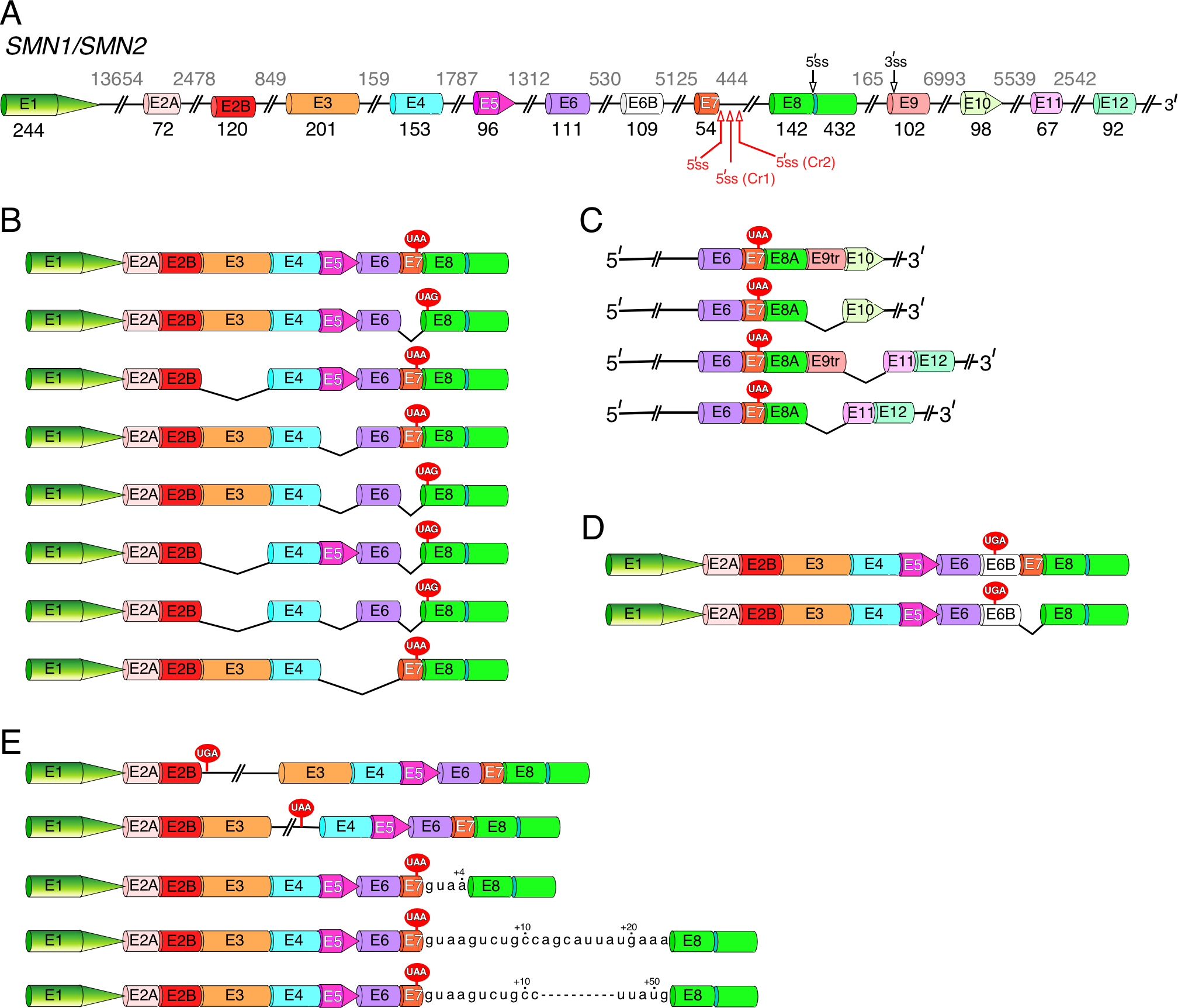
(A) Diagrammatic representation of SMN1/SMN2 pre-mRNA. Exons are shown as different colored shapes, introns, as broken lines. Exon sizes are indicated by numbers in black, intron sizes, by numbers in grey. Alternative and cryptic splice sites we identified are marked by black and red arrows, respectively. When applicable, the corresponding names of the cryptic splice site are given in parentheses. Abbreviation: E, exon; ss, splice sites. (B) Diagrammatic representation of the most common linear SMN splice isoforms generated by exon skipping. Skipped exons are indicated by black “V” shapes. The UAA and UAG stop codons located in exon 7 and exon 8, respectively, are shown. (C) Diagrammatic representation of linear SMN splice isoforms generated by inclusion of newly identified “intergenic” exons 9tr, 10, 11 and 12. Only the 3′-end exons are shown. Exon 9tr is a truncated version of exon 9 produced when the alternative 3′ss located in exon 9 (see (A)) is used. Exon 8A is a truncated version of exon 8 generated when the alternative 5′ss located in exon 8 (see (A)) is used. (D) Diagrammatic representation of linear SMN splice isoforms generated by inclusion of alternative exon 6B, together with or without exon 7. Inclusion of exon 6B will change the C-terminus of the SMN protein. (E) Diagrammatic representation of linear SMN splice isoforms with retained intronic sequences. Intronic sequences included due to activation of the cryptic 5′ss located in intron 7 are given. Usage of these cryptic sites increases the length of exon 7 by 4, 23 or 51 nucleotides.
