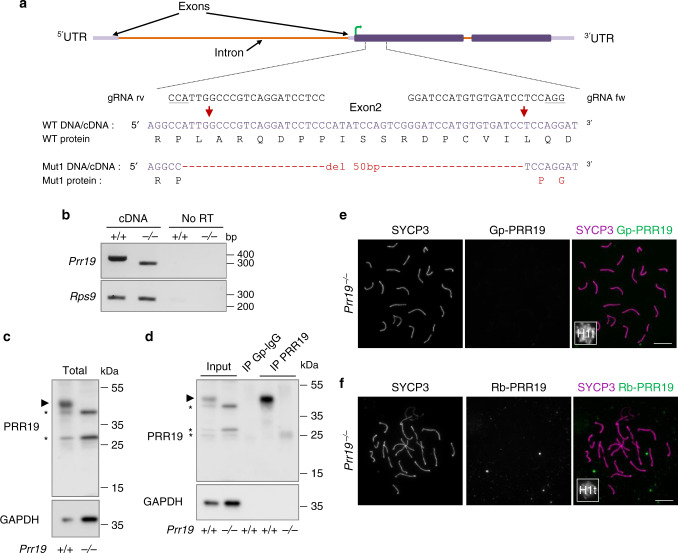
Fig. 2. The expression of PRR19 is disrupted in PRR19-deficient mice.
a Schematics of the Prr19 locus show exons, introns, translated regions (dark lilac boxes), untranslated regions (5′- and 3′-UTR, light lilac boxes) and the start of open reading frame (green arrow) in exon 2. Expanded view of exon 2 shows guide RNA sequences (gRNA rv and gRNA fw with PAMs underlined) used for CRISPR/Cas9 editing, the genomic DNA/cDNA sequence of the edited region and the corresponding protein sequences in wild-type (WT) and Prr19 mutant line (Mut1). DNA break sites are marked by red arrows; red text colour marks mutated DNA and protein sequences. The same 50-bp deletion was detected in both genomic DNA and cDNA from testis. b Agarose gel pictures show RT-PCRs using primers that match (upper panel) either Prr19 exon 1 and exon 2 sites flanking the targeted region, (lower panel) or, as a control, cDNAs of the 40S ribosomal protein S9 (Rps9). The total testis RNAs of adult wild-type (+/+) and PRR19-deficient (−/−) mice served as templates. Samples without reverse transcriptase (no RT) show RT-PCR specificity. DNA length marker positions are indicated. c, d Immunoblot analysis of (c) total protein extracts (Total), or (d) anti-PRR19 immunoprecipitations from testes of adult wild-type (+/+) and Prr19−/− (−/−) mice. d Pictures show inputs for immunoprecipitations, control immunoprecipitates with guinea pig IgG isotype antibodies (IP Gp–IgG) and immunoprecipitates with guinea pig antibodies against the C-terminal T183-Y366 peptide of PRR19 (IP PRR19). c, d Upper and lower panels show detection of proteins by guinea pig anti-PRR19 antibodies and, as loading control, anti-GAPDH antibodies, respectively. Arrowhead marks presumed band of PRR19 (40 kDa), asterisks mark unspecific protein bands in upper panels. Molecular weight marker positions are indicated. e, f Immunofluorescence showing SYCP3, PRR19 and histone H1t (miniaturised image) in nuclear surface-spread spermatocytes of adult Prr19−/− mice. Images show stainings with anti-PRR19 antibodies raised either in guinea pig (e) or rabbits (f). Refer to Fig. 1a and Supplementary Fig. 1d for the corresponding stainings in wild-type. Bars, 10 µm. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.