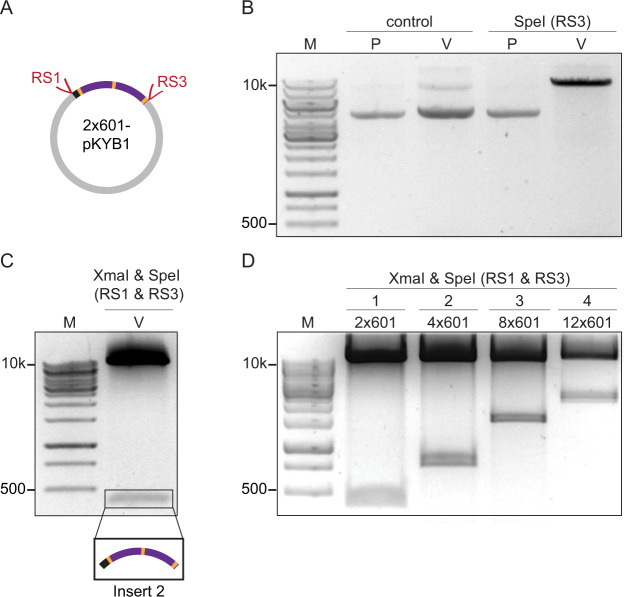
Figure 2.
Generation of inserts and plasmids containing arrays of n × 601 motifs obtained after sequential Gibson Assembly reactions. (A) Schematic illustration of Vector 1 (cf. Fig. 1A), consisting of two 601-core repeats (purple) flanked by 25 base pairs of linker DNA (yellow) embedded within a pKYB1 plasmid (resulting in a 2 × 601-pKYB1 vector). (B) Plasmids were screened for successful cloning by digestion at restriction site RS3 with SpeI and analysed by agarose gel electrophoresis (0.6% agarose gel), as shown here for one representative plasmid. Lanes 2 and 3 correspond to pKYB1 (P) and Vector 1 (V), respectively, while Lanes 4 and 5 correspond to the same plasmids following SpeI treatment. Only Vector 1 is digested by SpeI, confirming that this plasmid corresponds to the 2 × 601-pKYB1 vector. (C) The 2 × 601-pKYB1 plasmid is digested at restriction sites RS1 (with XmaI) and RS3 (with SpeI) to yield a 2 × 601 segment of 417 base pairs (Insert 2, cf. Fig. 1A). This segment was identified using agarose gel electrophoresis (1.5% agarose gel). (D) Agarose gel electrophoresis (1.5% agarose gel) of segments containing two, four, eight and twelve 601 motifs, digested from four different plasmids following four sequential Gibson Assembly reactions (labelled 1–4), as described in Fig. 1A.