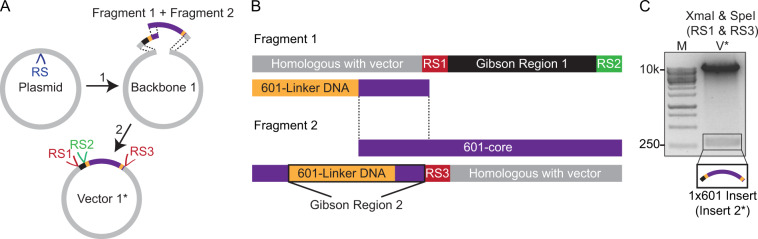
Figure 3.
Generation of plasmids containing integer numbers of 601 repeats with linker lengths of any size via Gibson Assembly reactions. (A) Insertion of a single 601 motif into a linearised plasmid via a three component Gibson Assembly reaction. Here, two DNA fragments (Fragment 1 and Fragment 2), that together form a single 601-core flanked by identical 601-linker sequences, are embedded in a suitable plasmid (Backbone 1). (B) Sequence composition of Fragments 1 and 2. Fragment 1 contains a 40 base pair region (purple) that is homologous to the 5’ end of Fragment 2 (highlighted by the dashed lines). Additionally, Fragments 1 and 2 each contain a 40 base pair region homologous to the 3’ and 5’ ends of Backbone 1, respectively (grey). These homologous regions enable the Gibson Assembly reactions depicted in panel A. Furthermore, Fragment 1 contains a Gibson Region 1, as well as two restriction sites (RS1 and RS2), while Fragment 2 contains a Gibson Region 2 and one restriction site (RS3). These are designed in such a way that, once both Fragment 1 and Fragment 2 have been incorporated into Backbone 1, further 601-based inserts can be generated by digestion of Vector 1* followed by Gibson Assembly reactions (analogous to that shown in Fig. 1A). (C) A pKYB1 plasmid containing a single 601-core sequence flanked by linker sequences of 50 base pairs was prepared using the approach outlined in panel A. This vector (V*) was digested at restriction sites RS1 (with XmaI) and RS3 (with SpeI) to yield a 1 × 601 segment (Insert 2*) of 303 base pairs. This segment was identified using agarose gel electrophoresis (1.5% agarose gel) and can be used for further Gibson Assembly reactions (cf. Fig. 1A).