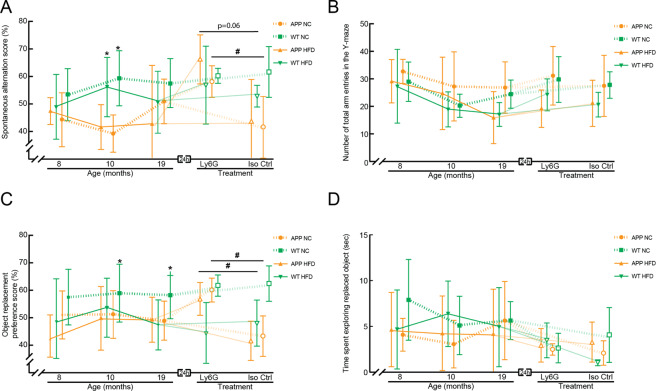
Figure 3.
Behavioral assays for short-term memory in APP/PS1 and WT mice on a Hfd or normal chow as a function of age and after treatment with α-Ly6G or Iso-Ctr antibodies. (A) Groupwise averages of spontaneous alternation score and (B) number of arm entries in the Y-maze taken at baseline for mice at 8, 10, and 19 months of age, and taken 24 hrs after α-Ly6G or Iso-Ctr antibody administration at the 19 month time point (4 mg/kg animal weight, intraperitoneal). (C) Groupwise averages of object replacement preference score and (B) time spent at the replaced object in the object replacement task taken at baseline for mice at 8, 10, and 19 months of age, and taken 24 hrs after α-Ly6G or Iso-Ctr antibody administration at the 19 month time point (4 mg/kg animal weight, intraperitoneal). Animal numbers for all measurements — 8 and 10 months: APP/PS1-NC: n = 6; WT-NC: n = 9; APP/PS1-Hfd: n = 10; WT-Hfd: n = 11; 19 months: APP/PS1-NC α-Ly6G: n = 5; APP/PS1-NC Iso-Ctr n = 4; WT-NC α-Ly6G: 7; WT-NC Iso-Ctr: 6; APP/PS1-Hfd α-Ly6G: n = 5; APP/PS1-Hfd Iso-Ctr: n = 5; WT-Hfd α-Ly6G: n = 4; WT-Hfd Iso-Ctr: n = 5. *p < 0.05 between genotypes (APP/PS1 vs. WT); #p < 0.05 between treatment groups (Ly6G vs. Iso-Ctr); Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA with post-hoc pair-wise comparisons using Dunn’s multiple comparison test.