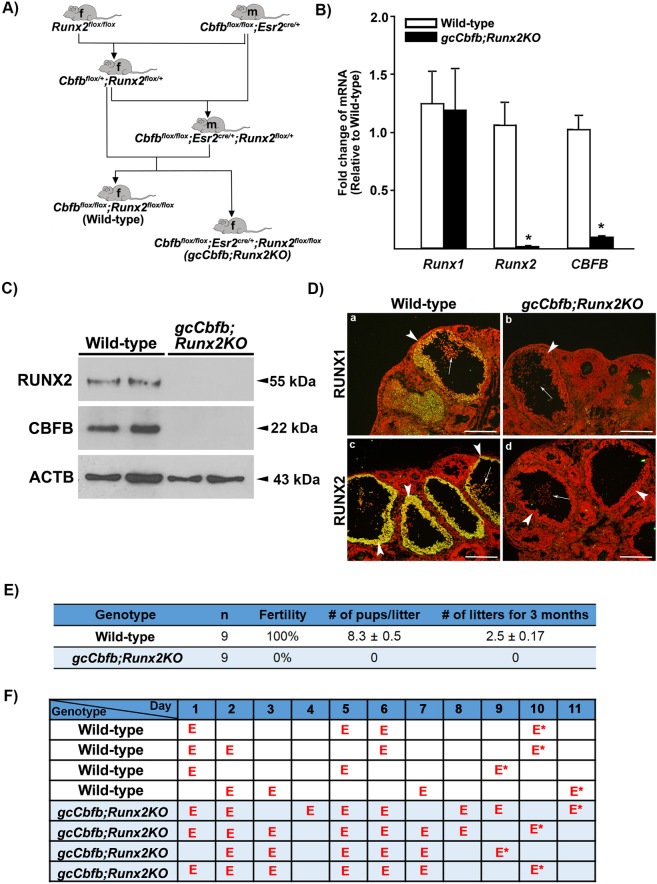
Figure 1.
Cbfbflox/flox; Esr2cre/+;Runx2 flox/flox (gcCbfb;Runx2KO) mice: Generation and verification of ovarian ablation of Runx2 and Cbfb expression and assessment of fertility and estrous cycling pattern. (A) Breeding schemes used to generate Cbfbflox/flox; Esr2cre/+;Runx2 flox/flox (gcCbfb;Runx2KO) and Cbfbflox/flox;Runx2 flox/flox (Wild-type) mice are depicted. F and M in the shape of mice represent female and male, respectively. (B) Granulosa cells were isolated from ovaries collected at 11 h post-hCG from PMSG-primed immature mice. Levels of mRNA for Runx1, Runx2, and Cbfb were measured by qPCR and normalized to the Rpl19 value in each sample (n = 8 animals/genotype). *p < 0.0001. (C) Western blot detection of RUNX2 and CBFB proteins in granulosa cells isolated at 11 h post-hCG. The membrane was re-probed with a monoclonal antibody against beta-actin (ACTB) to assess the loading of protein in each lane (n = 2 animals/genotype). (D) Immunohistochemical detection of RUNX1 and RUNX2 in ovaries of control and mutant mice collected at 11 h post-hCG (n = 3 animals/genotype). Immune-positive staining for RUNX1 or RUNX2 proteins (yellow/green) was localized to granulosa cells of periovulatory follicles in wild-type mice. Arrowheads and arrows point to granulosa cells and cumulus cells of preovulatory follicles, respectively. The sections were counterstained with propidium iodide (red) for nuclear staining. Scale bars, 250 μm for all images. (E) At 2 months of age, wild-type and gcCbfb;Runx2KO mice were mated with fertile males for 3 months. (F) Estrus cyclicity was monitored by daily vaginal smears for at least 2 cycles, and the presence of predominantly cornified cells was labeled as E (estrus). The animals were euthanized in the morning of estrus and marked E*.