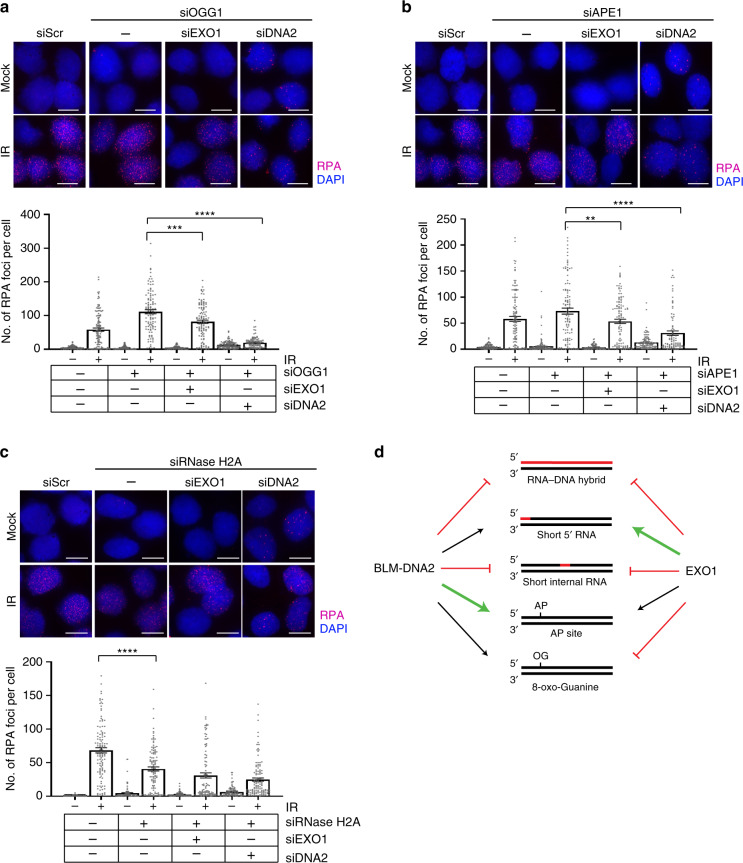
Fig. 6. Biological effects of 8-oxo-G residues, AP sites, and ribonucleotides.
a U2OS cells were depleted of OGG1 in combination with EXO1 or DNA2 knockdown using siRNA as indicated. Cells were screened for resection defects by quantifying IR-induced RPA foci 3 h after treatment with 6 Gy IR. Representative images of mock-irradiated or irradiated (IR) cells immunostained with anti-RPA antibody (red) are shown. Nuclei were stained with 4 ′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue). Plot shows average numbers of RPA foci per nucleus. b U2OS cells were depleted of APE1 in combination with EXO1 or DNA2 knockdown using siRNA, and assayed for resection defects as described above. c U2OS cells were depleted of RNase H2A in combination with EXO1 or DNA2 knockdown using siRNA, and assayed for resection defects as described above. All experiments were replicated n = 3 times, and all bars represent the mean. Error bars depict standard error of the mean. ** indicates p = 0.0068; ***, p = 0.0002; ****, p < 0.0001; two-tailed unpaired-t-test. The scale bar represents 10 μm for all images. d Model summarizing the effect of ribonucleotides, AP sites, and 8-oxo-G residues on resection. Black arrows indicate activity similar to that on control substrates devoid of any lesion, bold green arrows indicate stimulation of resection, and red perpendicular lines indicate attenuation of activity.