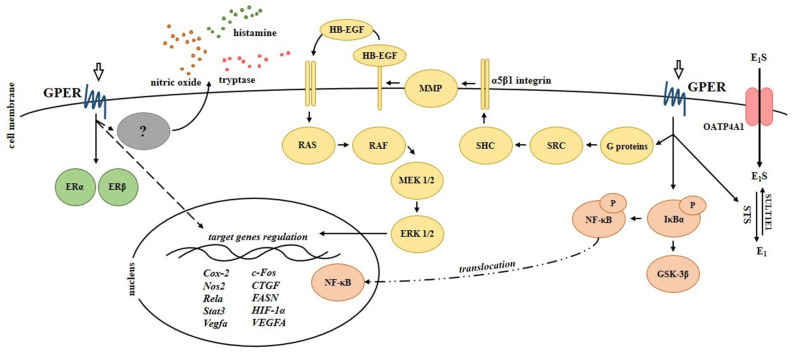
Figure 3.
Signaling pathways regulated by G protein-coupled estrogen receptor in the intestinal cells. Scheme shows experimentally proven signals mediated by GPER in bowel diseases. Cox-2, cycloxygenase-2; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; E1, estrone; E1S, estrone sulfate; ERα, estrogen receptor α; ERβ, estrogen receptor β; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK 1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; FASN, fatty acid synthase; c-Fos, FBJ osteosarcoma (subunit of AP1 transcription factor); GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β; HB-EGF, heparin-binding epidermal growth factor; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; IκBα, NF-κB inhibitor α; MEK 1/2, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; Nos2, nitric oxide synthase 2; OATP4A1, organic anion transporter polypeptide 4A1; P, phosphorylation; RAF, rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma (serine-threonine kinase); RAS, rat sarcoma (small GTPase); Rela, nuclear factor NF-κB subunit; SHC, adapter protein containing SRC homology 2 domain; SRC, non-receptor tyrosine kinase; Stat3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; STS, steroid sulfatase; SULT1E1, sulfotransferase family 1E member 1; Vegfa/VEGFA, vascular endothelial growth factor A.