FIGURE 3.
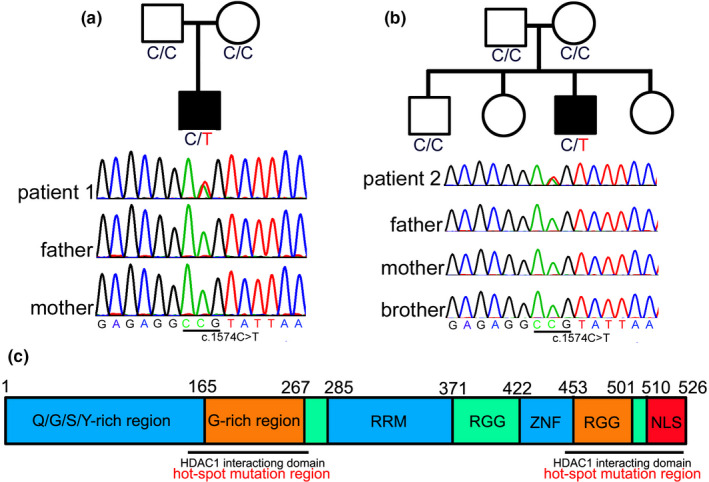
Genetic mutation of the patients. Genetic sequencing of patient 1 (a) and patient 2 (b) disclosed a mutation with c.1574C>T (p.P525L) in the FUS gene, while their parents or brother do not carry the variant, indicating the variant is a de novo mutation. Full‐length human FUS protein can be divided into Q/G/S/Y domain, G‐rich region, RNA recognition motif (RRM), two Arg‐Gly‐Gly (RGG)‐repeat regions interrupted by a zinc finger motif (ZNF), and nuclear localization signal (NLS). Structure–function analyses have shown that the G‐rich domain (amino acids 156–262) and C‐terminal domain (amino acids 450–526) of FUS are required for interaction of FUS and histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1), which harbor most of the ALS mutations (c)
