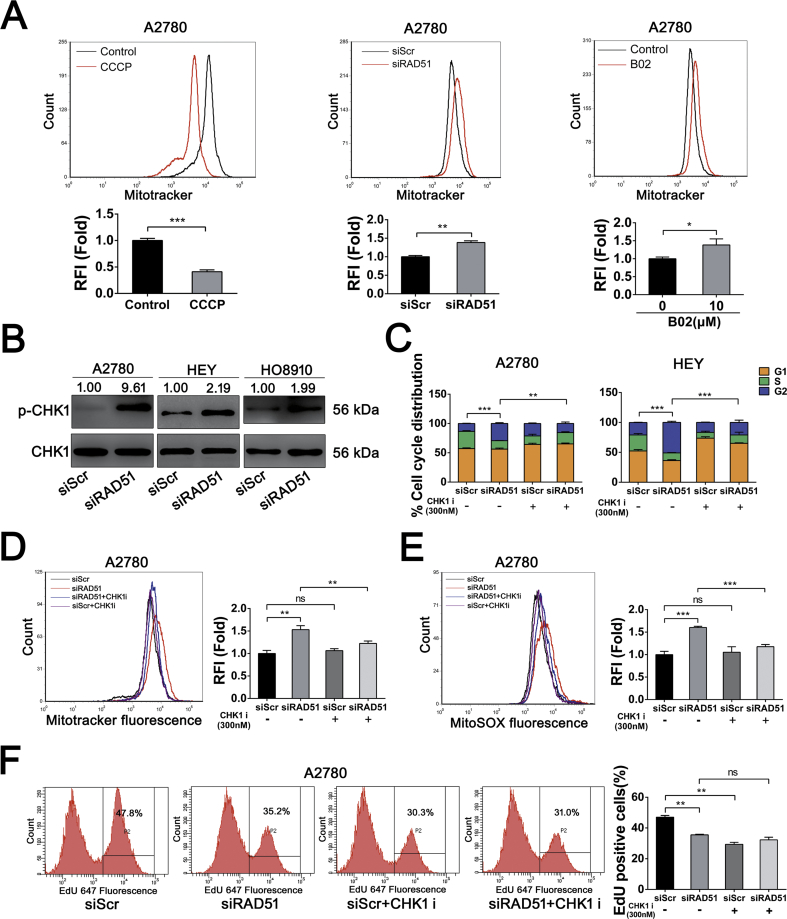
Fig. 6.
CHK1 activation-mediates the increased mitochondrial oxidative stress caused by RAD51 depletion. (A) Mitochondrial content decreased significantly after 12.5 μM CCCP treatment for 48 h (left). Mitochondrial content was elevated in A2780 cells after RAD51 knockdown (middle) or 10 μM B02 treatment (right), cells were stained with Mitotracker and quantified by flow cytometry. (B) Western blot analysis of phosphorylation of CHK1 in A2780, HO8910 and HEY cells after transfected siScr or siRAD51 for 48 h. CHK1 serverd as loading control. Band intensities were quantified by ImageJ. (C) Cell cycle distribution of A2780 and HEY cells transfected siScr or siRAD51 treated with or without 300 nM CHK1 inhibitor (UCN-01). The cell cycle distribution was measured by flow cytometry. (D) Mitochondrial content was quantified by flow cytometry in A2780 cells transfected siScr or siRAD51 treated with or without 300 nM CHK1 inhibitor (UCN-01). (E) MitoSOX distribution measured by flow cytometry in A2780 cells transfected siScr or siRAD51 treated with or without 300 nM CHK1 inhibitor (UCN-01). (F) EdU incorporation measured by flow cytometry in A2780 cells transfected siScr or siRAD51 treated with or without 300 nM CHK1 inhibitor (UCN-01). Data presented as mean ± S.D. are representative of three independent experiments. The statistical differences between the two groups were analyzed by two-sided unpaired Student's t-test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns stand for no significant).