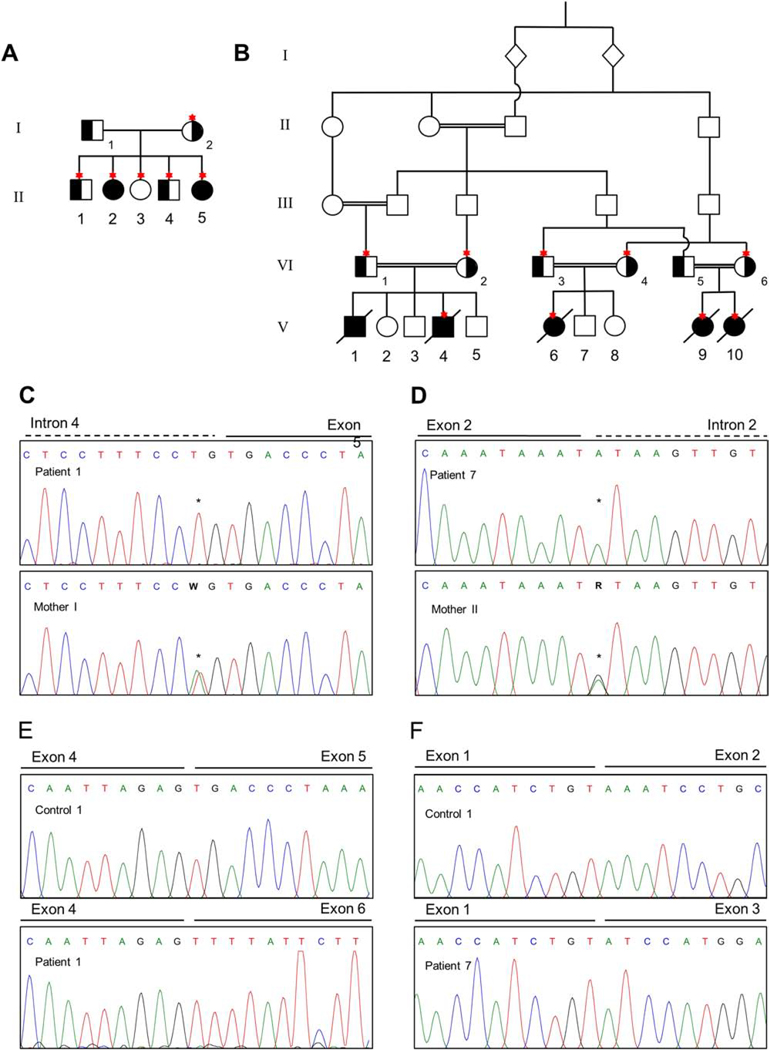
Figure 1. Pedigree and mutation analyses.
A. Pedigree for Family I showing the two affected sisters II-2 (patient 1) and II-5 (patient 2) and their nuclear family. Carrier status of the variant c.674–2A>T is indicated in black and Sanger confirmation was done for the individuals depicted with an asterisk. B. Pedigree for the consanguineous Family II showing the five affected 3rd cousins V-1 (patient 3), V-4 (patient 4), V-6 (patient 5), V-9 (patient 6) and V-10 (patient 7). Carrier status of the variant c.294+1G>A is indicated in black and Sanger confirmation was performed in the individuals depicted with an asterisk. C. Sanger confirmation of c.674–2A>T in Family I showing the affected patient 1 with a homozygous variant and an unaffected family member with a heterozygous variant. D. Sanger confirmation for c.294+1G>A in Family II showing the patient 7 with a homozygous variant and an unaffected family member with heterozygous variant. E. Chromatograms showing the effect of the variant c.674–2A>T in Family I resulting to the loss of exon 5 on cDNA level. F. Chromatograms showing the effect of the variant c.294+1G>A in Family II resulting in the loss of exon 2 on cDNA level.