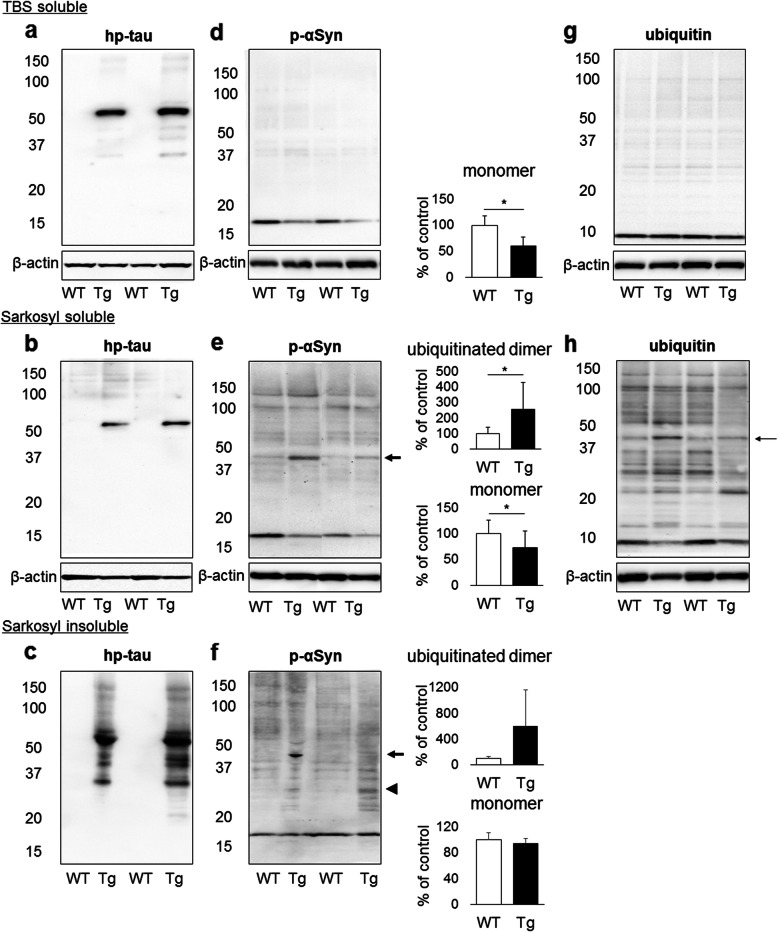
Fig. 4.
Western blotting analysis for hp-tau (AT8), p-αSyn (D1R1R) and ubiquitin in the TBS-soluble, sarkosyl-soluble, and sarkosyl-insoluble fractions from the hindbrain of rTg4510 mice (Tg) and control mice (WT) (n = 10 for TBS- and sarkosyl soluble fractions of Tg and WT mice, n = 3 for sarkosyl insoluble fractions of Tg and WT mice). A distinct band of hp-tau with a molecular weight of 50 kDa was detected in the TBS-soluble and sarkosyl-soluble fractions of Tg brains (a, b), and hp-tau was also detected in the sarkosyl-insoluble fractions of Tg brains (c). A single distinct band of p-αSyn monomers with a molecular weight of 17 kDa was detected in both mouse brains, and p-αSyn monomers were decreased in Tg brains (*p < 0.01, d). Additionally, p-αSyn oligomers were detected in the sarkosyl-soluble fractions of both mouse brains. p-αSyn monomers were decreased and ubiquitinated p-αSyn dimers with a molecular weight of 45 kDa (arrow) were increased in Tg brains (*p < 0.01, e). In addition to p-αSyn monomers, p-αSyn dimers (arrowhead) and ubiquitinated p-αSyn dimers (arrow) were detected in the sarkosyl-insoluble fractions of Tg brains (f). One distinct band of ubiquitin with a molecular weight of 10 kDa was detected in the TBS-soluble fractions of both mouse brains (g), and several bands of ubiquitinated proteins, including ubiquitinated p-αSyn dimers (arrow), were detected in the sarkosyl-soluble fractions of both mouse brains (h)