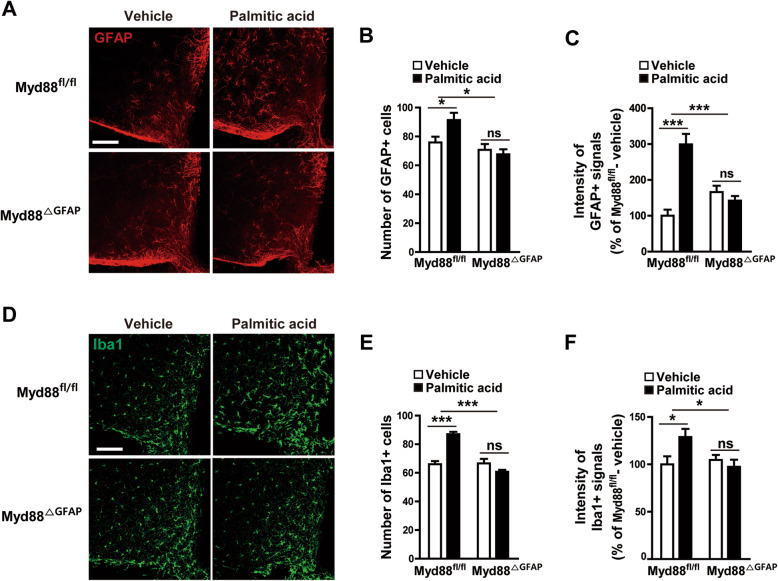
Fig. 3.
Palmitic acid–induced hypothalamic gliosis is attenuated by ablation of Myd88 expression in astrocytes. To identify the effect of astrocyte MyD88 on saturated free fatty acid–induced hypothalamic reactive gliosis, astrocyte-specific Myd88 KO mice (Myd88△GFAP) and control Myd88fl/fl mice were icv administered palmitic acid (50 pmol/2 μl), and their astrocytes and microglia were immunohistochemically analyzed with GFAP and Iba1 antibodies. a, d Representative images show palmitic acid–induced changes in hypothalamic GFAP-positive cells (a) and Iba1-positive cells (d) in Myd88fl/fl mice and Myd88△GFAP mice. b, c, e, f Number and intensity of GFAP-positive cells (b, c) and Iba1-positive cells (e, f) observed in the hypothalamic ARC of Myd88fl/fl mice and Myd88△GFAP mice after icv injection of palmitic acid or vehicle (n = 4–6 sections of 2–3 mice/group). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001. ns, not significant. Scale bar = 100 μm