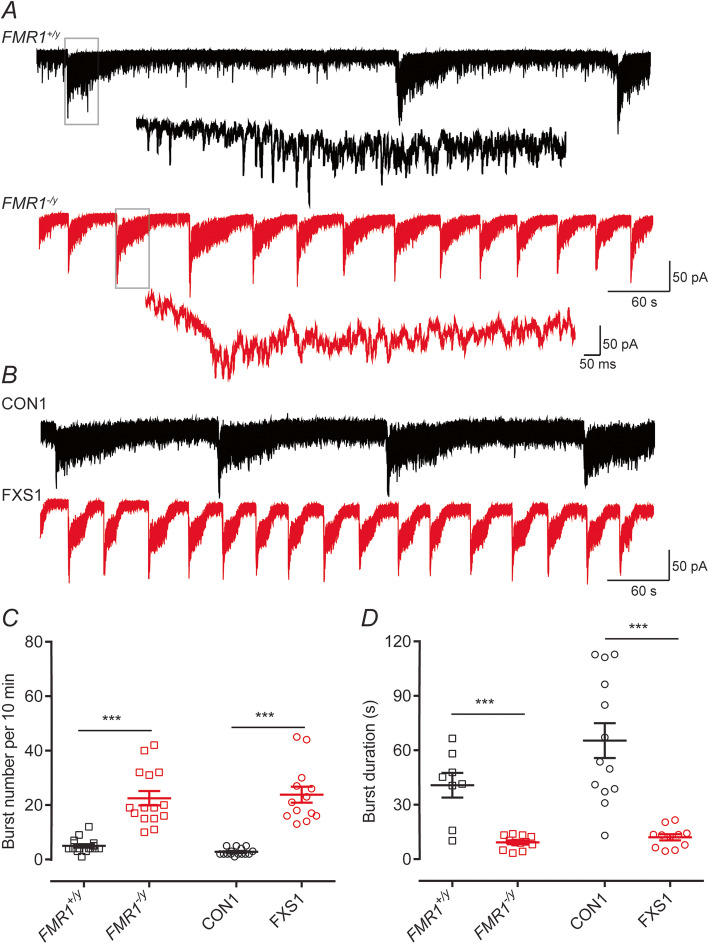
Fig. 3.
Neurons lacking FMRP display bouts of inward current activity of higher frequencies but of shorter durations compared to control neurons. a Representative voltage-clamp recording (Vhold = −70 mV) of spontaneous inward currents from either FMR1+/y (black) or FMR1−/y (red) neurons illustrating the difference in spontaneous events. The insets below, each trace illustrates an expanded time-base where evidence of synaptic currents underlying these inward currents can be observed. b As in a but illustration recordings from hiPSC lines CON1 (black) and FXS1 (red). c The number of events is higher in neurons lacking FMR1 than control. Overall, the mean number for bursts (per 10 min) are 4.5 ± 0.56 (FMR1+/y; n = 8, N = 3); 20.67 ± 3.96 (FMR1−/y; n = 12, N = 3); 2.8 ± 0.34 (CON1; n = 13, N = 3); 23.85 ± 2.92 (FXS1; n = 11, N = 3). d Mean burst durations recorded from neurons lacking FMRP are shorter than those from control lines. Overall, the mean durations are 40.72 ± 6.8 s (FMR1+/y); 9.28 ± 1.05 s (FMR1−/y); 59.90 ± 9.07 s (CON1); 11.52 ± 1.55 s (FXS1). ***p < 0.001, paired t test, Wilcoxon test