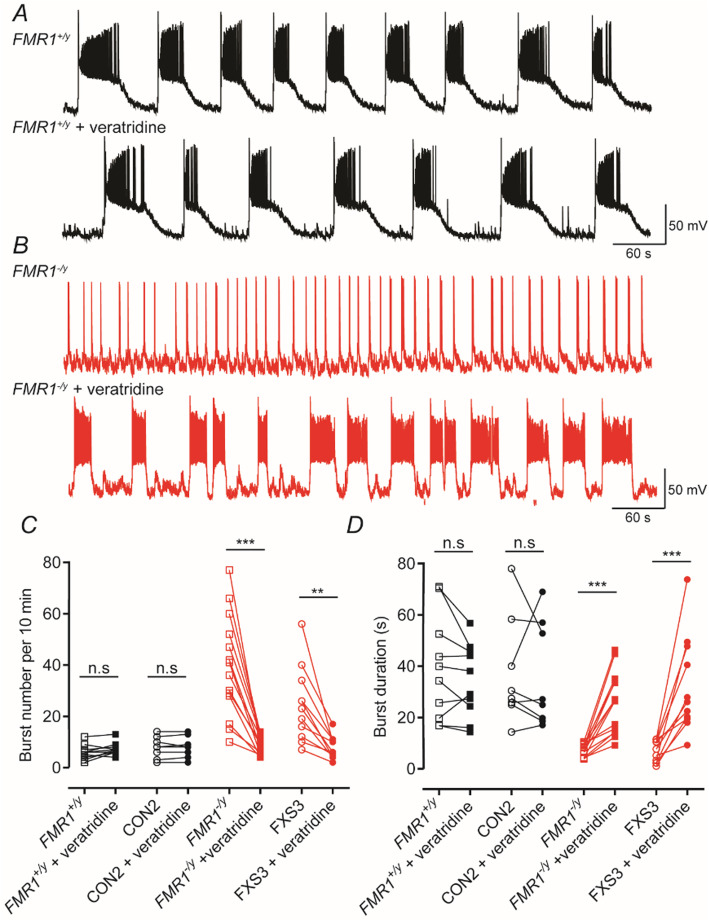
Fig. 5.
In neurons lacking FMRP activation of voltage-dependent Na+ channels decreases action potential burst frequencies but increases their duration. a Representative traces of a FMR1+/y neuron illustrating spontaneous action potential bursting before and after the application of veratridine (0.5 μM). b As in a but illustrating traces obtained from a FMR1−/y neuron. c Quantification of burst number in FMR1+/y, CON2, FMR1−/y and FXS3 lines before and after the application of veratridine. Veratridine reduced significantly the frequency of bursts in lines lacking FMRP. Overall, the mean number of bursts are 6 ± 0.92 (FMR1+/y, n = 10, N = 3); 7.3 ± 0.76 (FMR1+/y + veratridine, n = 10, N = 3); 7.87 ± 1.46 (CON2, n = 8, N = 3); 8 ± 1.45 (CON2 + veratridine, n = 8, N = 3); 39.29 ± 5.27 (FMR1−/y , n = 14, N = 3); 8.857 ± 0.98 (FMR1−/y + veratridine, n = 14, N = 3); 24.45 ± 4.37 (FXS3, n = 11, N = 3); 7.818 ± 1.32 (FXS3 + veratridine, n = 11, N = 3). d Quantification of action potential burst durations in each of the four lines examined. Veratridine increased significantly the duration of bursts in FMR1−/y and FXS3 lines and had no overall effect on FMR1+/y and CON2 lines. Overall, the mean burst durations are 39.09 ± 6.47 s (FMR1+/y); 34.34 ± 4.5 s (FMR1+/y + veratridine); 37.42 ± 7.39 s (CON2); 35.77 ± 7.25 s (CON2 + veratridine); 7.318 ± 0.64 s (FMR1−/y ); 25.5 ± 3.23 s (FMR1−/y + veratridine); 7.004 ± 1.28 s (FXS3); 32.26 ± 5.66 (FXS3 + veratridine). For both c and d, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, paired t test, Wilcoxon test