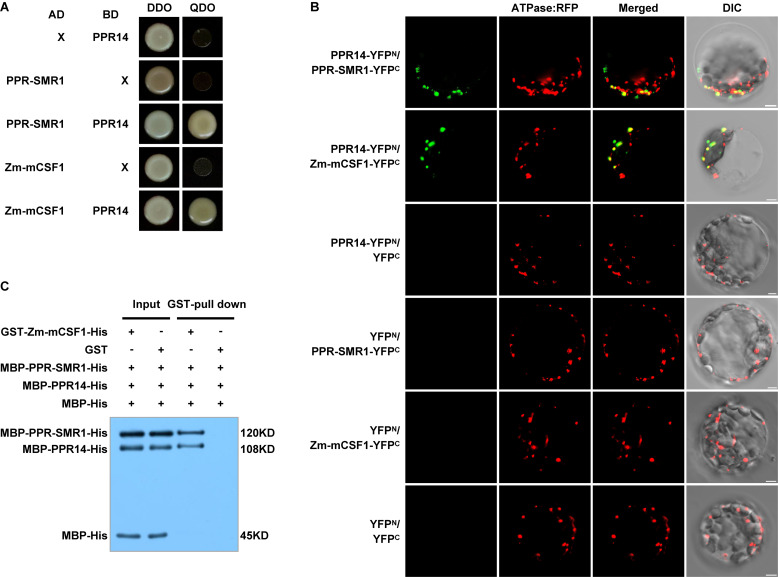
FIGURE 7.
PPR14 protein interacts with PPR-SMR1 and Zm-mCSF1. (A) Yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) analysis of PPR14 and PPR-SMR1 interaction, PPR14 and Zm-mCSF1 interaction. The Y2HGold strain harboring the indicated bait and prey constructs were spotted on synthetic dropout (SD)/-Leu-Trp (without Leu and Trp; DDO) and SD/-Ade-Leu-Trp-His (without Ade, Leu, Trp, and His; QDO). Yeast cultures on DDO control plates prove the existence of both plasmids. Positive interactions were verified by growth on QDO plates. (B) In vivo interactions between PPR14, PPR-SMR1, and Zm-mCSF1 proteins examined by BiFC. Yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) is split into N-terminus (YFPN) and C-terminus (YFPC). PPR14 is fused with YFPN, PPR-SMR1 and Zm-mCSF1 are fused with YFPC, respectively. The indicated combinations of -YFPN and -YFPC fusion proteins were transiently co-expressed in protoplasts of Arabidopsis leaves. Mitochondria were labeled by F1-ATPase-γ-RFP marker. Non-targeted YFPN and YFPC were used as negative controls. YFP signals and RFP signals were detected by a confocal laser microscope. Bars = 5 μm. (C) Pull-down assay for interactions between PPR14, PPR-SMR1, and Zm-mCSF1 proteins. Equal amounts of MBP-PPR14-His, MBP-PPR-SMR1-His, and MBP-His were combined with GST beads pre-incubated with GST-Zm-mCSF1-His or GST (input). Both input samples and pulled-down samples were analyzed by immunoblot with anti-MBP antibody. “ + ” and “−” indicate the presence and absence of corresponding proteins in the reactions, respectively.