Figure 2, Inhibition of Stat3 signaling attenuates IL-13 driven inflammation in SP-A−/− mice.
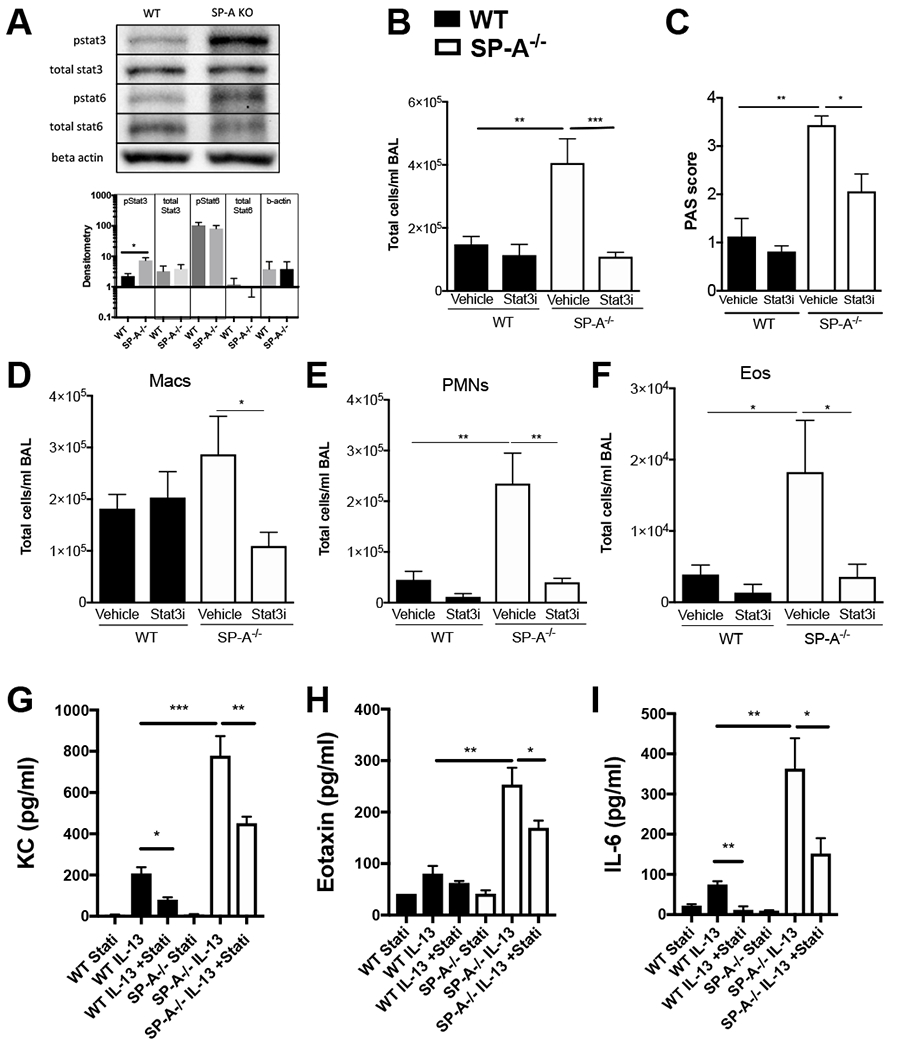
A) WT, SP-A−/− mice were exposed to IL-13 for 3 days and Stat3 and Stat6 phosphorylation was assessed from whole lung lystates by Western blot. n=8,8 lysates per group; representative bands shown from two independent blots. No Stat3 or Stat6 phosphorylation was detected in saline control treated mice. B-I) WT (black bars) or SP-A−/− (white bars) mice received vehicle or Stat3 inhibitor (5 mg/kg body weight) via ip injection 2 hrs prior to a one time airway challenge with IL-13. Twenty-four hours later, B) total cells in BAL were counted and C) mucin production was assessed from PAS stained histological sections. By differential staining, BAL cells consisted of D) macrophages (Macs), E) neutrophils (PMNs), and F) eosinophils (Eos). G) KC, H) Eotaxin and I) IL-6 were determined in BAL of SP-A−/− mice treated with and without Stat3 inhibitor prior to IL-13 by ELISA. n=8-12/per group, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
