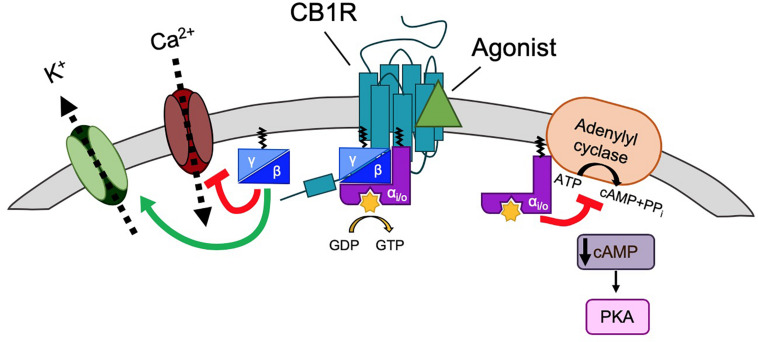
FIGURE 2.
G-protein signaling of CB1R. Classically, CB1R signaling is mediated by Gi/o signaling. CB1R is activated by ligand (green triangle), generating a conformational change that allows for heterotrimeric G-protein (α, β, and γ subunits) binding. The receptor then acts as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), activating Gα by GDP-to-GTP exchange. This triggers the dissociation of Gα from Gβγ. Gαi/o inhibits adenylyl cyclase (AC), a membrane protein that catalyzes that conversion of ATP to cAMP+PPi, causing a decrease in cAMP levels and thus inhibiting the PKA phosphorylation pathway. Gβγ inhibits voltage gated Ca2+ channels (VGCCs) and activates G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying K+ channels (GIRKs).