Fig. 3. Conformational ensembles accessible to apo and C-bound RAB as a function of Rp-cAMPS binding.
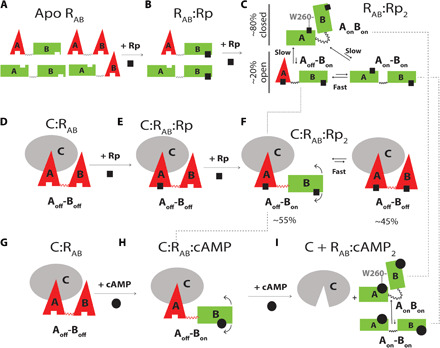
(A) States accessible within the degenerate free-energy landscape of apo RAB (20). Red triangles and green rectangles denote off and on conformations of each CBD, respectively. The on/off notation refers to the inability/ability of each CBD to promote inhibitory interactions of R with C. (B) States accessible to RAB:Rp. No interdomain interactions occur when CBD-A is apo. (C) States accessible to RAB:Rp2. The dashed lines indicate that the Aoff-Bon excited open state sampled by RAB:Rp2 is also sampled by C:RAB:Rp2 and is a transient intermediate along the cAMP-dependent activation pathway. (D and E) Rp binds first preferentially to CBD-A of C-bound RAB further stabilizing the inhibitory conformation of CBD-A. (F) States accessible to the quaternary complex C:RAB:Rp2, showing that when CBD-B is bound to Rp, it samples the “on” conformation as well. (G to I) Traditional sequential binding of cAMP to C:RAB, resulting in PKA activation. Unlike the case of Rp binding to C:RAB, cAMP binds first to CBD-B and then CBD-A (18). The dashed lines illustrate that the inhibition-incompetent RAB:cAMP2 complex samples the same ground states as RAB:Rp2 as well as one of the excited states.
