Fig. 4. Net interaction energies at assorted ionic strengths, and flux calculations.
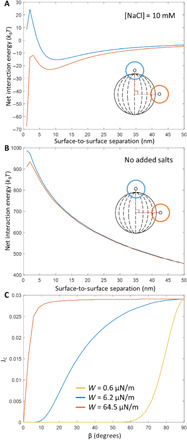
(A and B) Net interaction energy, φnet (W = 6.2 μN/m), calculated as a function of surface-to-surface separation between a probe colloid and polymerized bipolar microparticle (A) in the presence of aqueous 10 mM NaCl (Debye screening length = 3.04 nm) and (B) in the absence of added salts. In the absence of added salt, we measured the water to have a resistivity of 0.056 μS/cm at 25°C, from which we calculated the Debye screening length to be 458 nm (equivalent to a 1:1 electrolyte at concentration of 440 nM). Orange corresponds to the probe colloid near the equator of the bipolar microparticle; blue represents an approach near the poles. (C) Flux of probe colloids onto the surfaces of bipolar microparticles, calculated using Eq. 2 with surface potentials of −50 mV and the indicated anchoring energies for different angles of incidence.
