Fig. 4. TRA2A binds to the YS-M and PR8-NS mRNA through GAAARGARR motif.
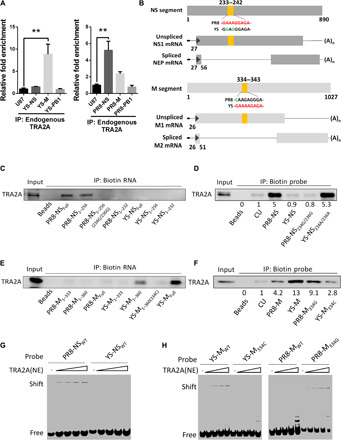
(A) A549 cells were infected with either the YS (left) or PR8 (right) virus at an MOI of 1 for 12 hours. RIPs and RT-qPCR were performed using specific primers detecting viral M, NS, and PB1 mRNA and cellular U87 small Cajal body-specific RNA (scaRNA). Fold enrichment of mRNA was calculated. Means ± SD (error bars) of three independent experiments are indicated (**P < 0.01). (B) Schematic illustration of the TRA2A binding sites in M and NS mRNA. (C and E) TRA2A bound to biotin-labeled YS or PR8 NS (C) or M (E) mRNAs or their truncated mRNAs. In vitro transcribed mRNAs were labeled with the biotin and immunoprecipitated with the NEs, and the bead eluate was then analyzed by Western blotting. (D and F) Pull-down TRA2A proteins using 20-bp NS (D) or M (F) biotin probes of PR8 and YS: Probes were immunoprecipitated with the NEs, and the bead eluate was analyzed by Western blotting. (G) TRA2A binding efficiency to PR8-NSWT and YS-NSWT was compared in RNA EMSA with increasing amounts of NEs. (H) TRA2A binding efficiency to YS-MWT and YS-M334C (left) and PR8-MWT and PR8-M334G (right) was compared in RNA EMSA with increasing amounts of NEs.
