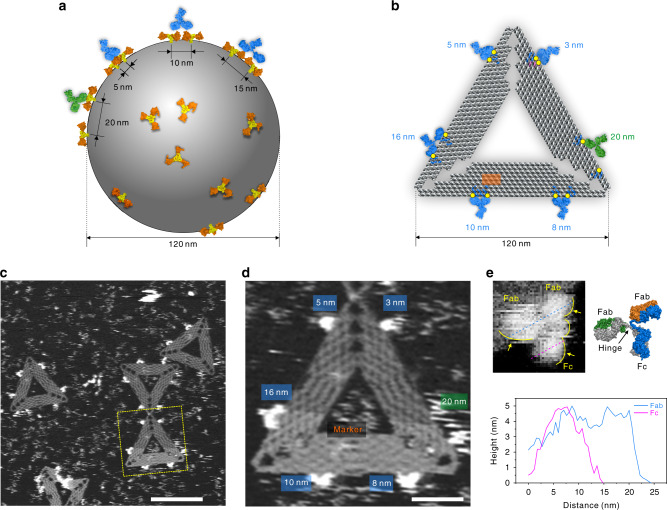
Fig. 1. DOE-based capture of IgGs.
a Schematic representation of non-even distribution of epitope spikes on the surface of a viral particle. b Designed, virus-mimicking DOEs for IgG capture and binding. Artificial epitope (digoxin, yellow), DNA origami (gray), modified staple DNA strands (blue and pink), IgGs (bivalent binding, blue; monovalent binding, green). c PeakForce-AFM image for DOE-based capture of IgGs. Scale bar, 100 nm. d Enlarged view of the dashed yellow square in panel c. Scale bar, 20 nm. e A high-resolution HS-AFM image of an Fc and two Fab domains of the bound IgG (upper left, yellow arrows); atomic structure of IgG (Protein Data Bank (PDB) entry 1HZH, upper right); cross-sectional profile of three domains (Fab, blue and Fc, magenta) in a DOE-bound IgG (bottom). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.