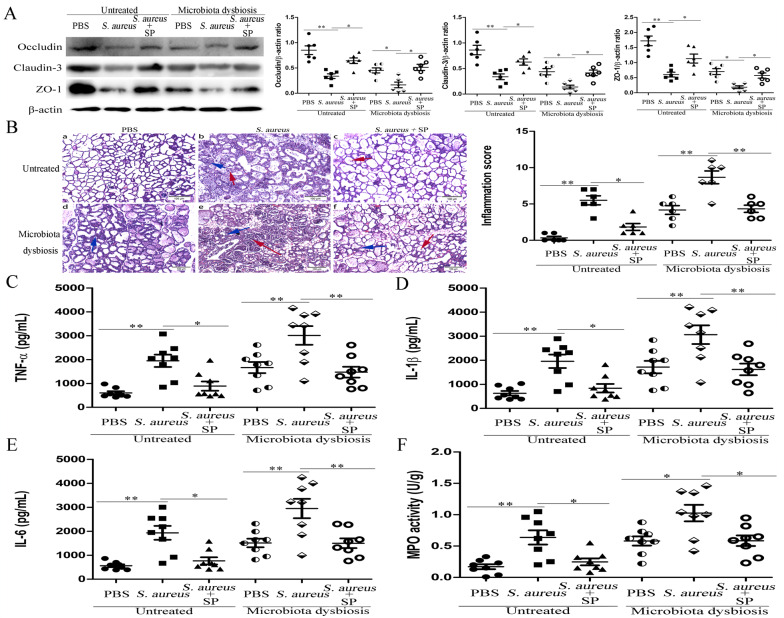
Fig. 3. Sodium propionate (SP) protects against S. aureus-induced mastitis by regulating blood-milk barrier permeability.
Mice were administered an intraperitoneal injection of sodium propionate (SP, 100 mg/kg) 1 h before infection with S. aureus (1 × 107 CFU). Twenty-four hours later, mammary gland tissues were collected and used for testing. a Expression of tight junction proteins, including Occludin, Claudin-3, and ZO-1, was tested 24 h after infection in untreated and gut microbiota-dysbiosis mice. b Mammary gland tissue sections of untreated and gut microbiota-dysbiosis mice were stained with H & E (100×). The black arrow was the normal tissues. The red arrow was the infiltration of inflammatory cells. The blue arrow was the hyperplastic of alveolar wall. Levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α (c), IL-1β (d), and IL-6 (e), as well as MPO activity (f) in mammary glands was assessed 24 h after infection in untreated and gut microbiota-dysbiosis mice. The results are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 6–8); *p < 0.05 is significantly different from each group.