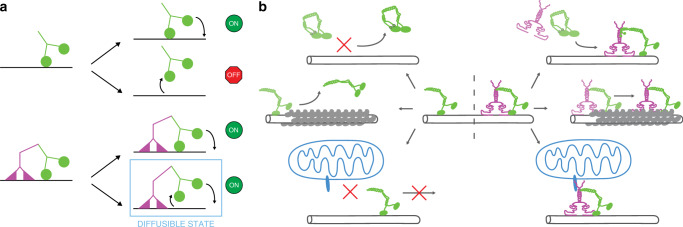
Fig. 6. Schematic illustration of the TRAK1-mediated anchoring of KIF5B.
a Top: in absence of TRAK1, KIF5B (green) can either continue its walk by rebinding the disengaged motor domain to the microtubule or dissociate from the microtubule when the engaged motor domain unbinds from the microtubule. Bottom: in presence of microtubule-bound TRAK1 (magenta), when both motor domains of KIF5B disengage from the microtubule, KIF5B remains tethered to the microtubule through a diffusive interaction of TRAK1 with the microtubule and thereby enables the rebinding of a motor domain of KIF5B to the microtubule. In this state, TRAK1 might facilitate navigation around obstacles by diffusion along the microtubule surface. b Overview of the functions of TRAK1. Top: TRAK1 activates auto-inhibited KIF5B, enabling its processive movement along microtubules. Middle: TRAK1 increases the processivity of KIF5B in crowded environments. Bottom: TRAK1 enables KIF5B-based transport of isolated mitochondria along microtubules in vitro.