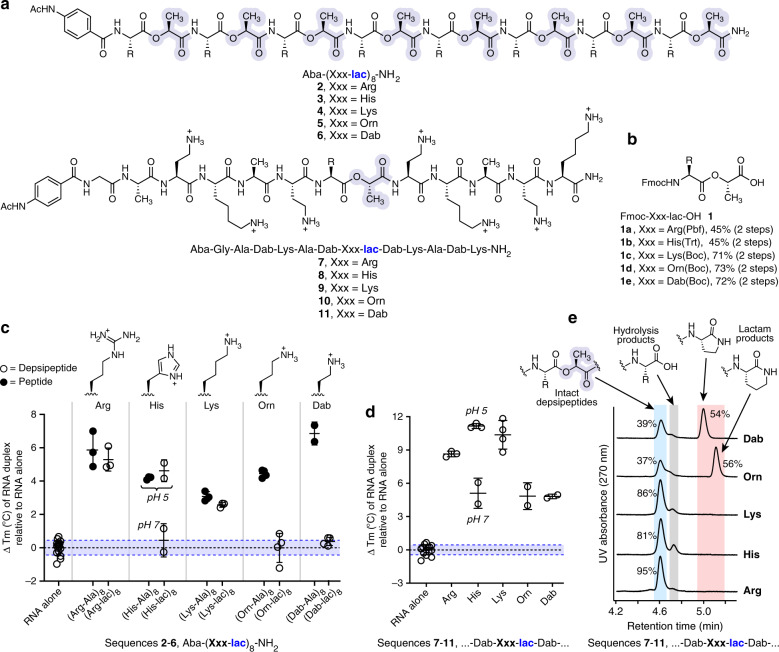
Fig. 3. Structure–function studies of cationic depsipeptides in stabilizing an RNA duplex.
Each sample contained RNA duplex 1 (5′-rCrGrCrUrArArArUrCrG-3′ and 5′-rCrGrArUrUrUrArGrCrG-3′, 2.5 μM strand) and peptide/depsipeptide (100 μM) in buffered solution (10 mM phosphate, 100 mM NaCl, pH 7.0 or 10 mM acetate, 100 mM NaCl, pH 5.0). a Structures of depsipeptides used to systematically characterize cationic side chain effects on RNA duplex stability. Lactic acid residues are highlighted. Ac acetyl, Aba acetamidobenzoic acid, which was appended to the N-terminus to increase UV absorbance. b Structures of the Fmoc-didepsipeptide building blocks used for solid-phase synthesis of depsipeptide sequences. Fmoc fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl. c Comparative effects of oligo-didepsipeptide sequences 2–6 and analogous oligo-dipeptide and on the Tm of the RNA duplex (number of independent measurements: n = 3 for Arg and Lys sequences; n = 2 for His and Dab sequences; n = 4 for Orn sequences). The shaded areas correspond to the mean ± SD Tm measured for the RNA duplex alone (n = 16 independent measurements). Data are shown as a scatter plot with mean ± SD. d Comparative effects on RNA duplex Tm of depsipeptide sequences containing a single backbone ester (number of independent measurements: n = 3 for Arg; n = 2 for His, Orn, and Dab; n = 4 for Lys), relative to RNA duplex alone (n = 16 independent measurements). Data are shown as a scatter plot with mean ± SD. e To assess the impact of different cationic side chains on depsipeptide degradation rates, depsipeptides 7–11 (40 μM) were incubated at 37 °C in buffer (100 mM HEPES, 10 mM NaCl, pH 7.3). After 5 min, the reactions were quenched by the addition of 3% TFA, and samples were analyzed by HPLC. Consistent with the hypothesis that sequences containing Orn or Dab adjacent to a backbone ester bond would undergo facile intramolecular O,N acyl transfer, only 37–39% of the starting depsipeptide remained, predominantly due to the formation of lactam products. In contrast, intramolecular degradation products were not observed for the sequences containing Arg, His, or Lys adjacent to the ester bond, and >80% of the intact depsipeptide were observed in these cases.