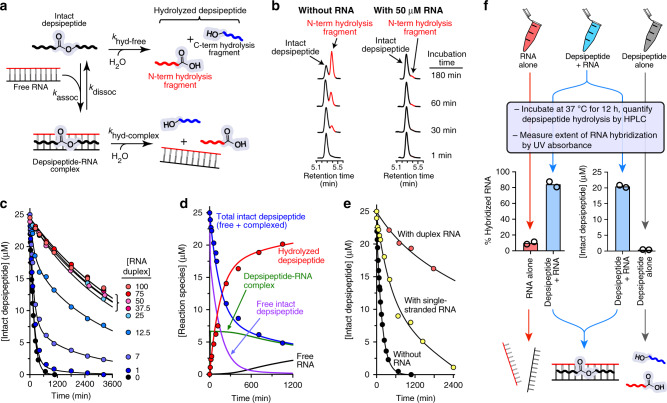
Fig. 5. RNA increases the hydrolytic lifetime of a cationic depsipeptide.
a A schematic of depsipeptide-RNA interactions leading to increased depsipeptide lifetimes. The free depsipeptide is hydrolyzed with a pseudo-first rate constant, khyd-free. Binding of the depsipeptide to RNA is governed at equilibrium by kassoc/kdissoc. The pseudo-first rate constant for of depsipeptide hydrolysis within the depsipeptide–RNA complex is khyd-complex. Under conditions where complex formation is favorable and khyd-complex < khyd-free, the presence of RNA will increase the depsipeptide lifetime. b HPLC traces (270 nm) showing hydrolysis of depsipeptide 9 (25 μM) at various time points in the presence or absence of RNA duplex 1 at 37 °C in pH 7.3 buffer. The C-terminal fragment of the hydrolyzed depsipeptide is not observed because it lacks the Aba chromophore. (c) Time courses for hydrolysis of depsipeptide 9 (25 μM) with varying concentrations of the RNA duplex 1. The curves shown are from simultaneous fits of data to the model given in panel a using SimFit44. During fitting, we fixed kassoc = 1 × 105 M−1 s−1. Therefore, three rate constants were fit, with values obtained by the fitting of: khyd-free = 1.1 × 10−4 s−1, khyd-complex = 3.2 × 10−6 s−1, and kdissoc = 8.3 × 10−3 s−1. d Kinetic profile of the hydrolysis reaction of depsipeptide 9 (25 μM) in the presence of 7 μM RNA duplex 1. Observed data are shown as filled circles, while the curves represent concentrations of molecular species predicted by SimFit modeling. e Comparison of depsipeptide hydrolysis in the absence of RNA, or in the presence of single-stranded RNA (100 μM 5′-rCrGrArUrUrUrArGrCrG-3′) or RNA duplex 1 (50 μM each strand). f To illustrate the mutually increased depsipeptide lifetime and RNA duplex Tm, three samples were prepared in parallel: one containing only RNA duplex 1 (25 μM each complementary strand), one containing only depsipeptide 9 (25 μM), and one containing both the RNA and 9 (at a 1:1 molar ratio). The extent of depsipeptide hydrolysis and RNA hybridization were then measured. Data are shown as a scatter plot of two independently repeated experiments.