Figure 3.
PRMT1 Regulates Progesterone Signaling, Inhibiting the Phosphorylation and the Proteasomal Degradation of PR
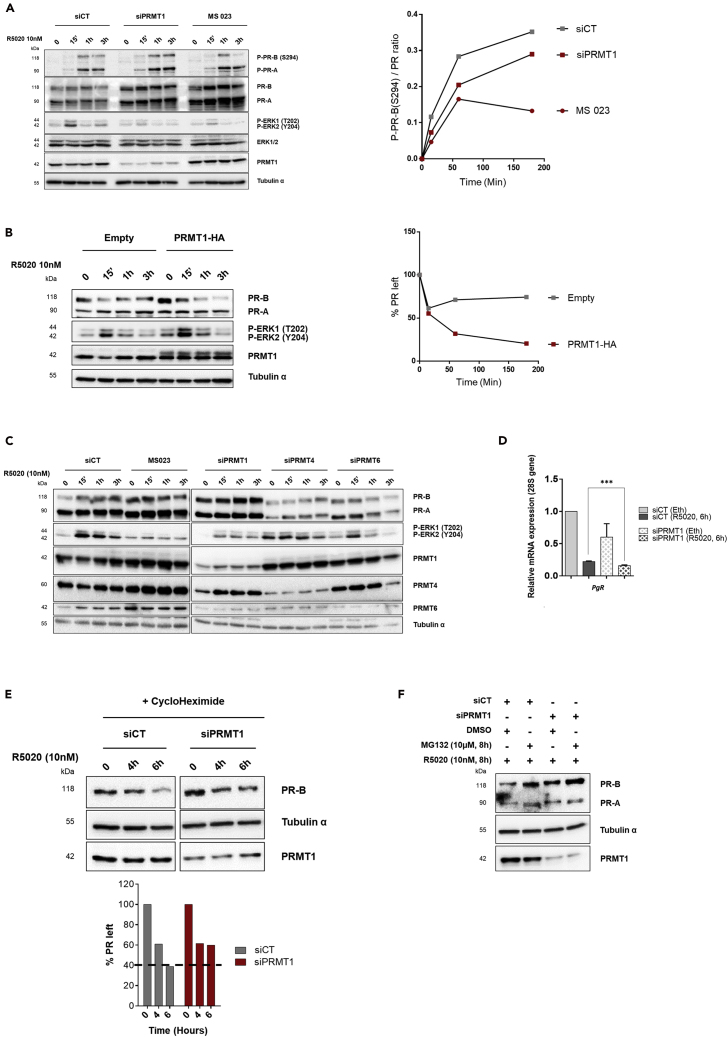
(A) WB of T47D cells silenced for PRMT1 (siPRMT1) or transfected with siRNA control (siCT), or treated with MS 023 (60 nM), and stimulated with R5020 (10 nM) for the indicated times (left). Quantification of phospho-PR [P-PR-B (S294)] band intensity relative to total PR-B was measured by ChemiDoc MP (Biorad). The ratio was calculated for each time point and is shown graphically (right).
(B) WB of T47D cells transfected with HA-PRMT1 or empty-HA plasmids and treated with R5020 (left). Quantification of PR-B band intensity for each time was measured by ChemiDoc software (Biorad) (right).
(C) WCE from T47D cells, depleted for PRMT1, PRMT4, or PRMT6 by specific siRNA pool or treated with 60 nM of MS 023 inhibitor, then stimulated with R5020, were analyzed by IB.
(D) RT-qPCR of PR mRNA from T47D cells, transfected with siPRMT1 or with siCT and treated with R5020 (10 nM) for 6 h. The mean ± SEM of at least three experiments is shown. Mean values were normalized against the expression of 28S ribosomal mRNA as reference. The p value was calculated using a paired t test: ∗∗∗ indicates p ≤ 0.001.
(E) Half-life study of endogenous PR-B protein. Lysates from T47D cells depleted or not for PRMT1 as in (A) were collected at the indicated time points after addition of cycloheximide and subjected to IB (top). The amount of PR-B was quantified by densitometry using the ChemiDoc software (Biorad).
(F) T47D cells were transfected with siCT or with siPRMT1 and treated with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (10 μM) for 8 h or vehicle DMSO, before R5020 treatment. WCE were analyzed by IB. IB quantifications were done for one experiment, representative of three independent ones.