Figure 1.
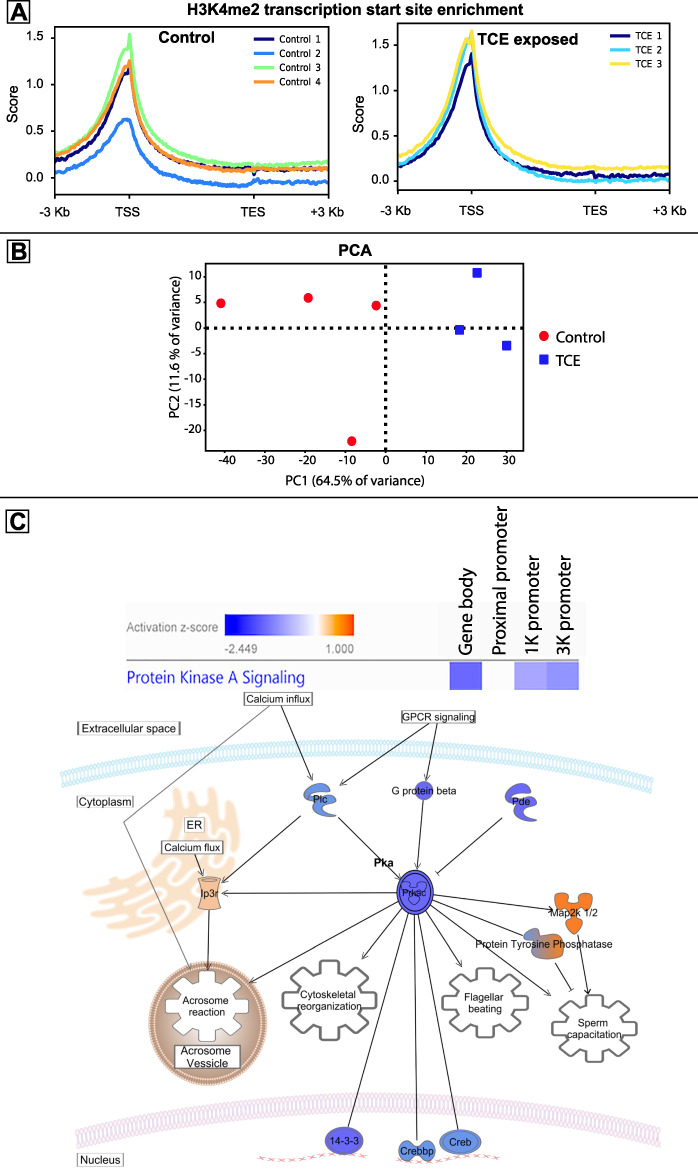
Altered demethylated H3K4me2 localization in rat sperm after exposure to TCE. (A) Enrichment of H3K4me2 as measured by normalized read counts scaled to each gene in the rn4 rat genome, their TSS, TES, and 3000 nucleotides upstream and downstream of the genes. (B) PCA shows how the first two PCs account for most of the variation in the samples. (C) IPA software found protein kinase A (Pka) signaling genes had significant decrease in number of H3K4me2 peaks in the gene body, 1-k promoter, and 3-k promoter regions. IPA pathway builder illustrates the biological relation of genes that are epigenetically altered after TCE exposure. Blue shows where fewer H3K4me2 were found near the genetic loci for the respective gene in TCE compared to controls and orange shows where more H3K4me2 were found. The blue–orange gradient denotes opposite findings in the different gene regions. Two known sperm stimuli, calcium influx, and Zona pellucida binding to g-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) feed into the PKa signaling pathway. The PKa signaling pathway stimulates four known sperm functions, including: the acrosome reaction, cytoskeletal reorganization, flagellar beating, and sperm capacitation.
