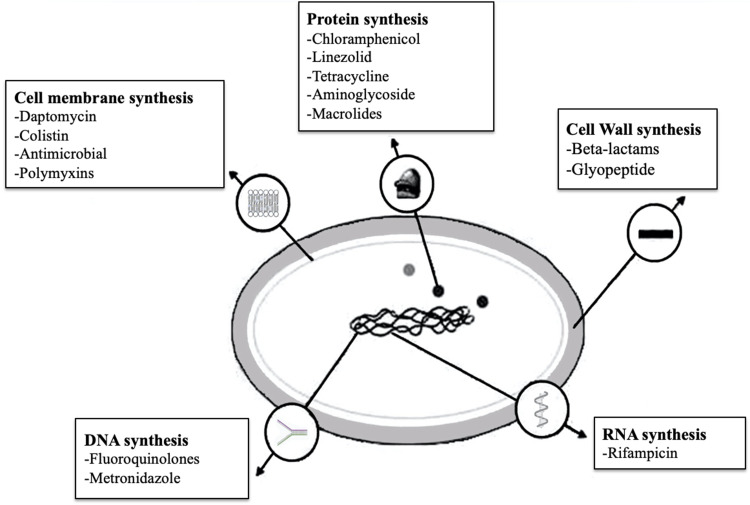
Figure 1.
Overview of bacterial antibiotic resistance mechanisms. Antibiotics target essential bacterial processes and structures to inhibit cell growth and/or causing cell death. The major cellular targets for antibiotics include DNA replication (eg, fluoroquinolones), protein synthesis (eg aminoglycosides), cell wall integrity (eg, penicillins) and folic acid metabolism (eg, sulfonamides).