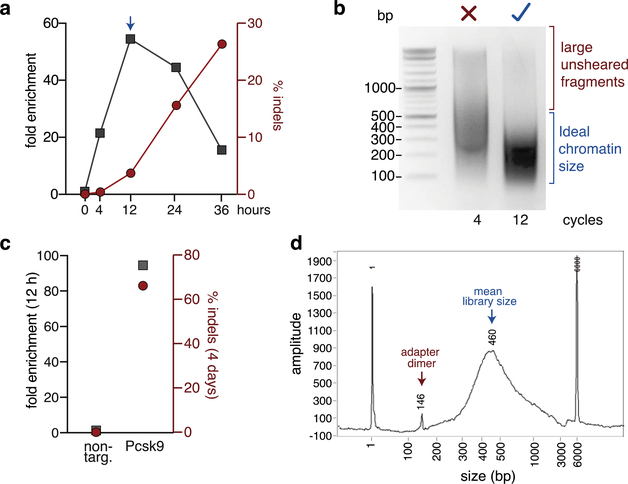
Figure 3: Quality controls of a DISCOVER-Seq experiment.
(a) Example of a ChIP-qPCR time course to determine the ideal time point for DISCOVER-Seq using a Cas9 RNP (Box 2). K562 cells were nucleofected with Cas9 and gRNA targeting the HBB locus. Cells were then crosslinked at indicated time points and MRE11 ChIP performed. Shown is the fold enrichment of the on-target region (HBB) over a negative control region for each sample (left y-axis) and the indel frequencies (right y-axis). For this experiment 12 h post nucleofection was chosen as the ideal time point for DISCOVER-Seq (arrow). (b) Agarose gel electrophoresis of insufficiently (4 cycles) and optimally (12 cycles) sheared chromatin. Sheared chromatin size (150–500 bp) should be checked after sonication before proceeding with the protocol (Box 3). (c) Example of quality control by qPCR for successful isolation of an on-target locus by ChIP before proceeding to ChIP-Seq library preparation. B16-F10 cells were nucleofected with a non-targeting gRNA (non-targ.) or a gRNA targeting Pcsk9. After 12 h, cells were crosslinked and MRE11 ChIP was performed. Shown is the fold enrichment of the on-target site Pcsk9 over a negative control region (left y-axis) and the indel frequencies after 4 days (right y-axis). (d) Example electropherogram of a ChIP-Seq library before sequencing. While the mean library size is optimal, this sample contains adapter dimers. If adapter dimers are present, DNA size selection of the library should be performed (see ?Troubleshooting).