Extended Data Fig. 5. Usp22 Regulates Foxp3 through Transcriptional Mechanisms.
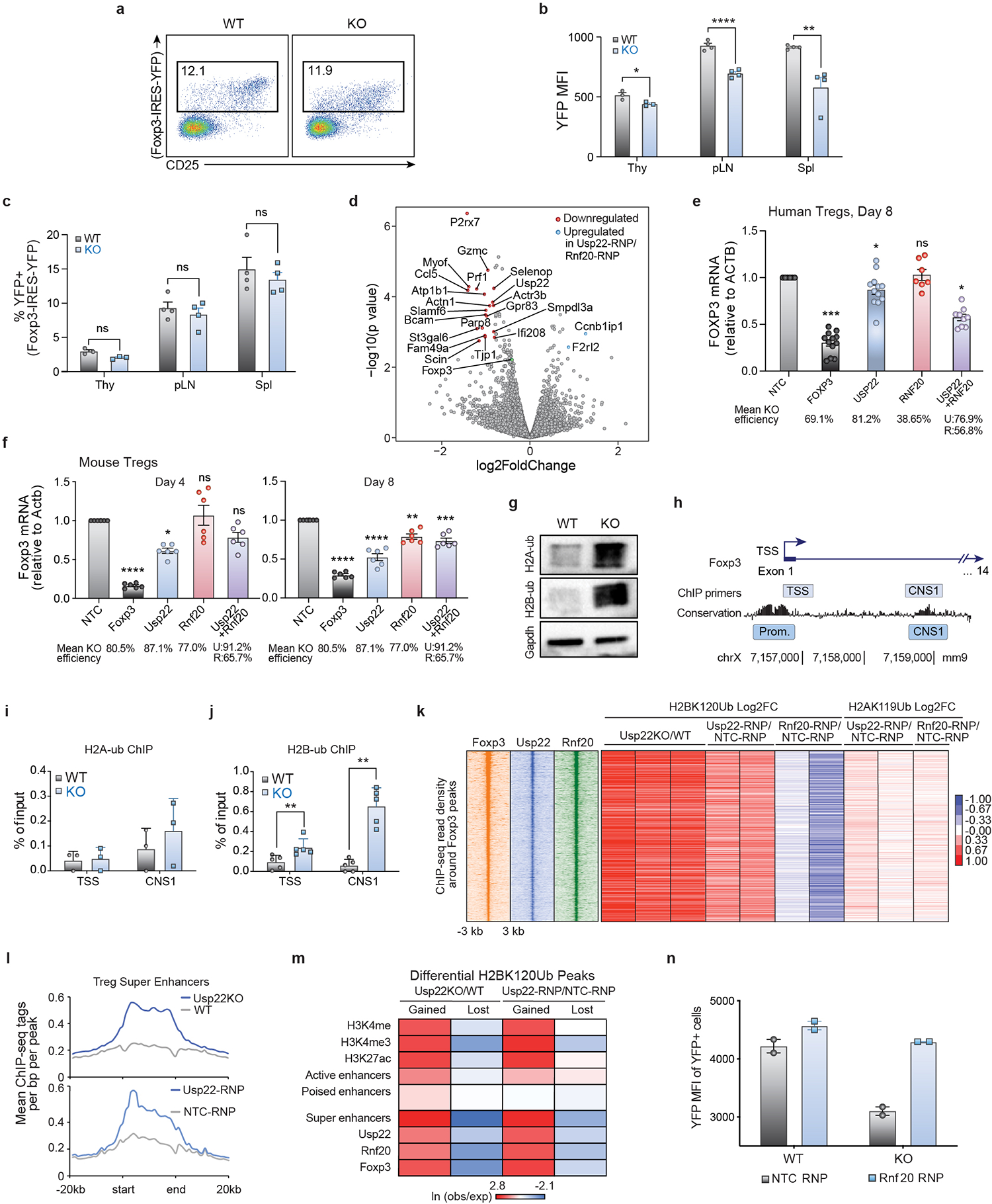
a) Representative flow cytometry analysis of the YFP+ Treg population (gated on CD4+ cells) from the spleen and lymph nodes of Usp22+/+Foxp3YFP-Cre WT or Usp22fl/flFoxp3YFP-Cre KO mice.
b) Statistical analysis of YFP MFI in CD4+YFP+ Tregs from the thymus (Thy), peripheral lymph nodes (pLN), and spleen (Spl) of Usp22+/+Foxp3YFP-Cre WT or Usp22fl/flFoxp3YFP-Cre KO mice.
c) Statistical analysis of CD4+YFP+ Treg frequencies in Usp22+/+Foxp3YFP-Cre WT or Usp22fl/flFoxp3YFP-Cre KO mice, corresponding to panel b.
d) Volcano plot for RNA sequencing of Usp22 RNP KO Tregs vs Rnf20 RNP KO murine Tregs. X-axis shows log2FoldChange (LFC). Y-axis shows the –log10 of the p-value as calculated by DESeq2. Genes downregulated in the Usp22 RNP KO compared to Rnf20 RNP KO are shown in red and genes upregulated are shown in blue defined by p-value <5e-3 and LFC > 0.8. Foxp3 (shown in green) trended down but did not reach significance.
e) qPCR analysis of FOXP3 mRNA levels in human Tregs from 2 donors 8 days post-electroporation with Cas9 RNPs targeting NTC , FOXP3, USP22, RNF20 or both USP22 and RNF20. Normalized to the expression of β-ACTIN transcripts. Data are presented as mean ±SEM and are representative of at least two independent experiments.
f) qPCR analysis of Foxp3 mRNA levels in mouse Tregs 4 and 8 days post-electroporation with Cas9 RNPs targeting NTC, Foxp3, Usp22, Rnf20 or both Usp22 and Rnf20. Normalized to the expression of β-actin transcripts.
g) Western blot analysis of ubiquitinated histone 2A (H2AK119Ub; H2A-ub) and ubiquitinated histone 2B (H2BK120Ub; H2B-ub) from iTregs from Usp22+/+Foxp3YFP-Cre WT or Usp22fl/flFoxp3YFP-Cre KO mice. Gapdh was used as a loading control. Source data can be found in Supplementary Figure 1.
h) Schematic of Foxp3 locus depicting PCR products used for ChIP-qPCR data shown in panel i and panel j.
i) ChIP-qPCR data analysis for H2AK119Ub (H2A-ub) where primers amplified across the transcriptional start site (TSS) and the CNS1 enhancer region of the Foxp3 locus. Data are normalized to the input and are presented as mean ±SD.
j) ChIP-qPCR data analysis for H2BK120Ub (H2B-ub) for PCR across the transcriptional start site (TSS) and across the CNS1 enhancer region of the Foxp3 locus. Data are normalized to the input and are presented as mean ±SD.
k) Heatmap of ChIP-seq read density for Foxp3, Usp22, and Rnf20 at sites bound by Foxp3 (using previously published Foxp3 ChIP data35), ranked by highest to lowest Foxp3 binding signal. The corresponding log2 fold change (log2fc) for either H2BK120Ub or H2AK119Ub upon Usp22 or Rnf20 deletion at these sites are plotted on the right, with each biological replicate shown as an individual column.
l) Average ChIP-seq read density of H2BK120Ub at Treg super enhancers in control versus Usp22-deficient Tregs.
m) Co-occurrence analysis showing the natural log of the ratio of the observed number of overlapping regions over the expected values for sites that either gain or lose H2BK120Ub in Usp22-deficient Tregs against publicly available histone modifications H3K4me, H3K4me3 and H3K27ac as well as enhancer classes, as described in the Methods.
n) Analysis of reciprocal regulation of Foxp3 by deubiquitinase Usp22 and E3 ubiquitin ligase Rnf20. YFP MFI of Tregs sorted from Usp22+/+Foxp3YFP-Cre WT or Usp22fl/flFoxp3YFP-Cre KO mice and then electroporated with either NT control (NTC-RNP) or Rnf20 RNP, corresponding with Figure 2j where Foxp3 MFI from the same experiment is shown.
All data are presented as mean ±SEM, unless otherwise stated. ns indicates no significant difference, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. The exact sample sizes (n), p-values, statistical tests and number of times the experiment was replicated can be found in the “Statistics and Reproducibility” section.
