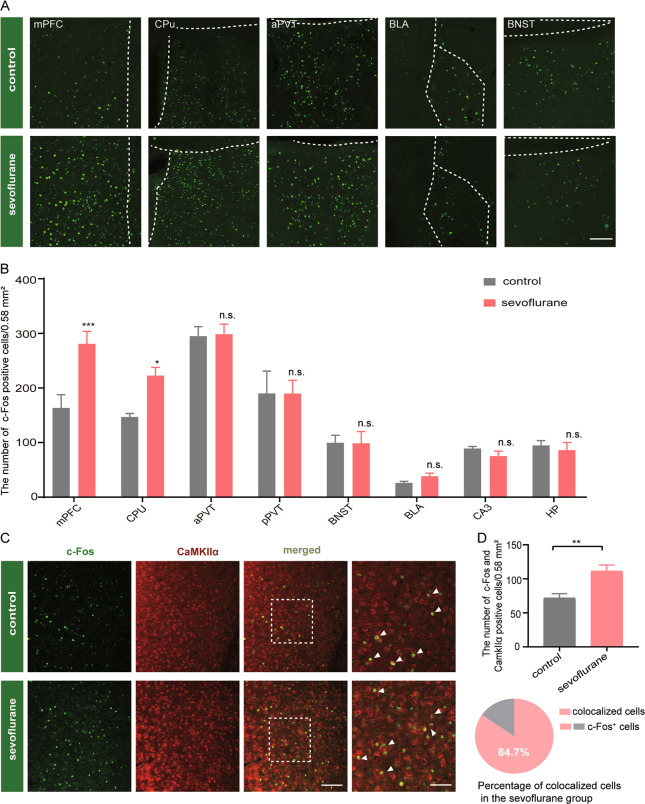
Fig. 2. Enhanced mPFC neuronal activities are associated with the sevoflurane-induced impulsivity.
a Representative images show the c-Fos-positive cells in mPFC, CPu, aPVT, BLA, BNST from control (top), and sevoflurane (bottom) mice. Scale bar, 100 mm. mPFC, medial prefrontal cortex; CPu, caudate putamen, striatum; aPVT anterior paraventricular thalamic nucleus; pPVT posterior paraventricular thalamic nucleus; BLA basolateral amygdaloid nucleus; BNST bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. (dotted line show the boundary of brain area). b Quantification of c-Fos positive cells in the mPFC, CPu, aPVT, pPVT, BNST, BLA, CA3, and HP, respectively. HP, hypothalamus area. The number of c-Fos expression in the mPFC is markedly higher for sevoflurane mice (n = 6, Two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni multiple comparison post hoc tests). c Representative micrograph showing the c-Fos+ neurons (green), CaMKIIα+ neurons (red) and colocalized cells. Scale bar (left) 100 μm; (right) 50 μm. (arrows = double-labeled cells). d Quantification of the number of c-Fos+ neurons that colocalized with CaMKIIα+ neurons (top). Percentage of CaMKIIα+ cells expressing c-Fos in the sevoflurane mice (bottom). (n = 6; Unpaired Student’s t test). Data = mean ± SEM; n.s. no significance, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.