Fig. 4.
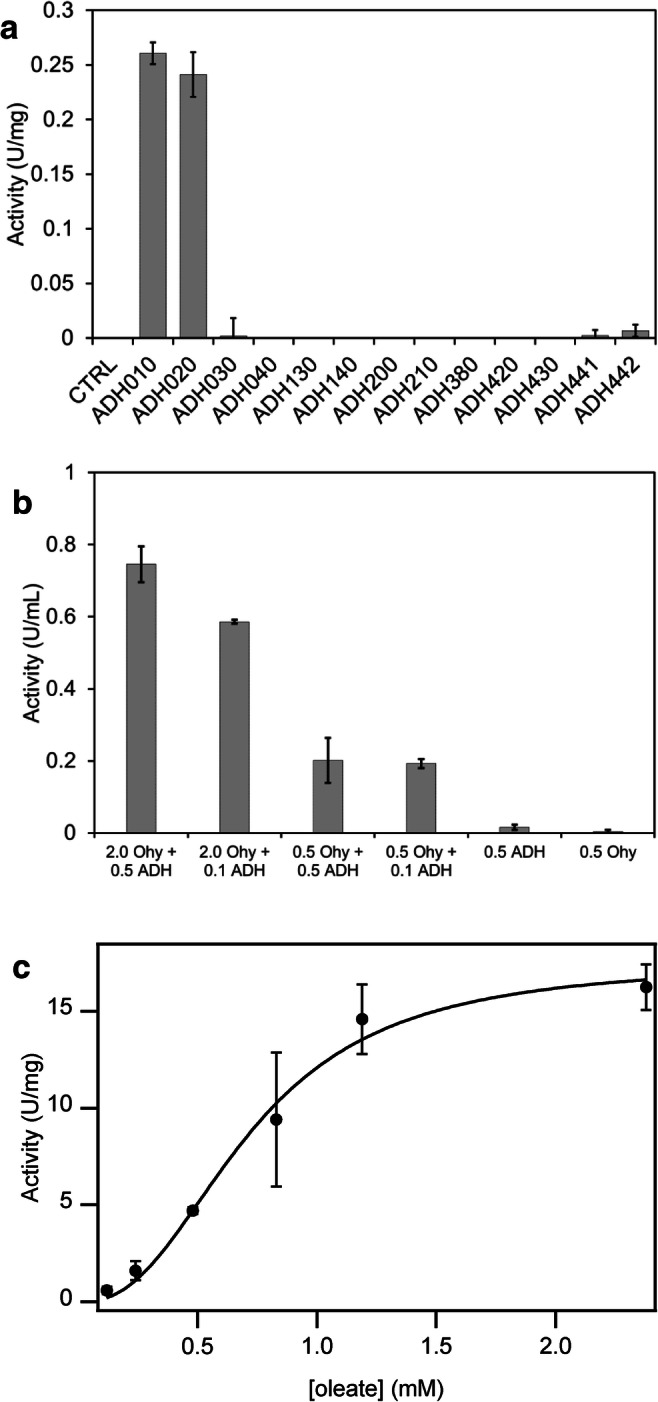
Assay development and kinetics of RpOhy. a Screening of ADHs for the coupled assay of Ohy catalyzed conversion of oleic acid. Reaction conditions: 0.47 mg/ml ADH (lyophilised powder), 2.5 mM 10-hydroxystearic acid, 2 mM NAD+, 20 mM PIPES buffer pH 6.5 and 10% DMSO. b Validation of the Ohy-ADH coupled assay using Em-OAH1. Enzyme amounts below the horizontal axis are given in mg/ml protein for Em-OAH1 and mg/ml lyophilised powder for AHD010. Reaction conditions: 0–0.5 mg/ml ADH010, 0–2 mg/ml Em-OAH1, 2.5 mM oleic acid, 2 mM NAD+, 50 mM PIPES buffer pH 6.5 and 10% DMSO. c Apparent cooperative kinetics of RpOhy measured in a coupled assay with ADH010. Assay conditions: 0.125–2.5 mM oleic acid, 2 mM NAD+, 50 mM PIPES pH 6.5 and 10% DMSO, 0.3–1.5 μg/ml RpOhy and 0.01–0.5 mg/ml ADH010. The solid line is a fit to the cooperative kinetics Hill equation with K0.5 = 0.72 ± 0.07 mM and Vmax = 17.5 ± 1.4 U/mg, n = 2.45 ± 0.47
