Figure 7.
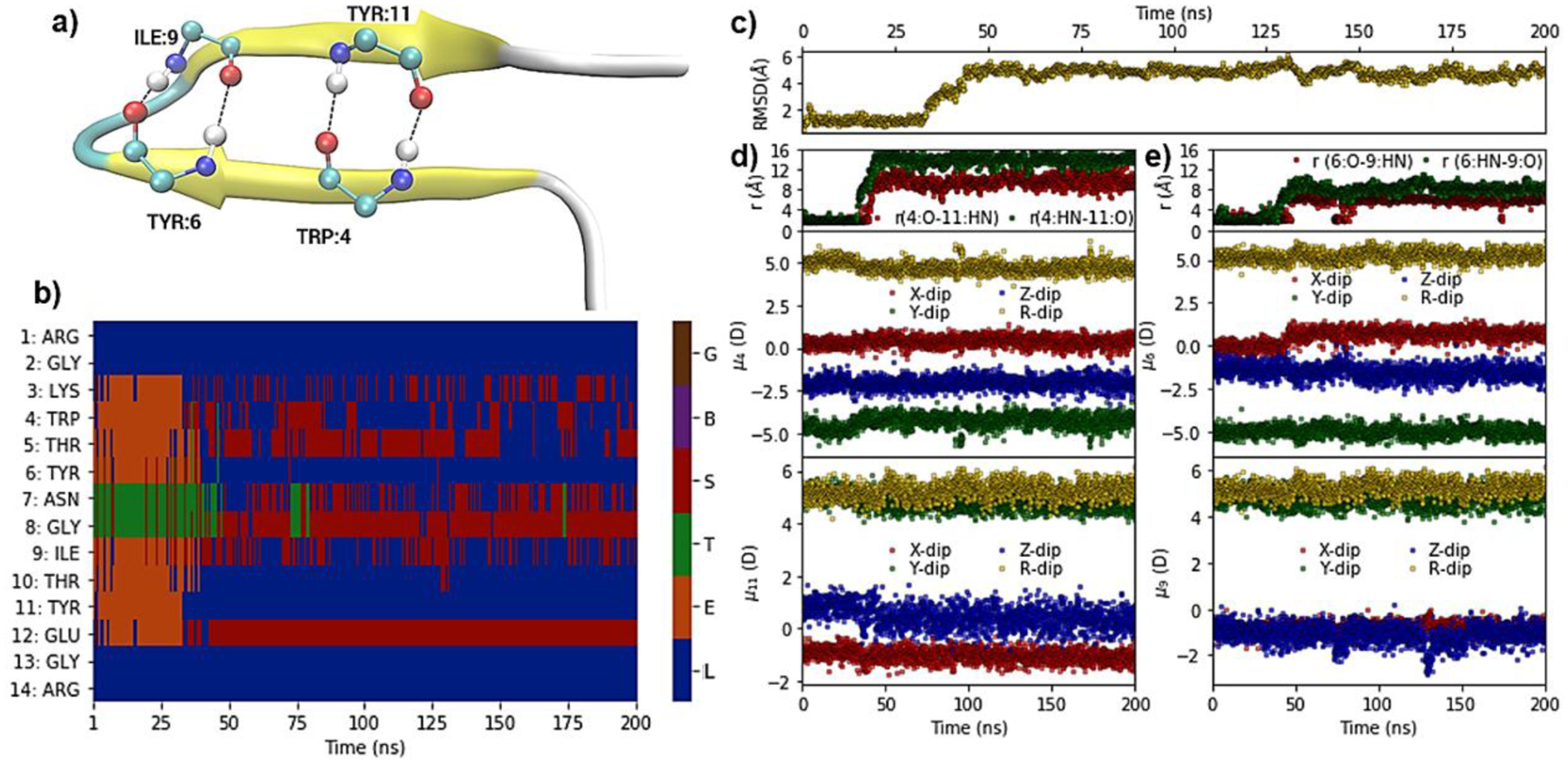
Hydrogen-bond, structural, dipole and DSSP based secondary structure analysis of a simulation of the MBH 12 protein (PDB ID: 1K43) at 370 K. (a) Pictorial representation of crystal structure of MBH 12, with hydrogen-bond interactions between peptide bond carbonyl oxygen (O) and nitrogen hydrogen (HN) of residues TRP:4, TYR:6, ILE:9, and TYR:11. (b) Heatmap showing DSSP-defined secondary structures versus time. (c) RMSD with respect to the NMR structure for Cα atoms versus time. (d) Upper panel: Distance between TRP4:O-TYR11:HN (red) and TRP4:HN-TYR11:O atoms versus time; middle and lower panels: Dipole moment components (μx, μy, μz) and total dipole moment (μR) of peptide backbone (C,O,N,HN,Ca,Ha) for TRP4 and TYR11, respectively, versus time. (e) Upper panel: Distance of TYR6:O-ILE9:HN (red) and TYR6:HN-ILE9:O versus time; middle and lower panels: Dipole moment components (μx, μy, μz) and total dipole moment (μR) of peptide backbone for TRP4 and ILE9, respectively, versus time. The DSSP assignment codes are H: Alpha helix, B: Residue in isolated beta-bridge, E: Extended strand, participates in beta ladder, G: 3/10 helix, I: pi helix), T: hydrogen bonded turn and S: bend, while L indicates loops or irregular/random coil elements.
