Figure 5. Structural modules of DrBphP and RTKs used for opto-RTK modeling.
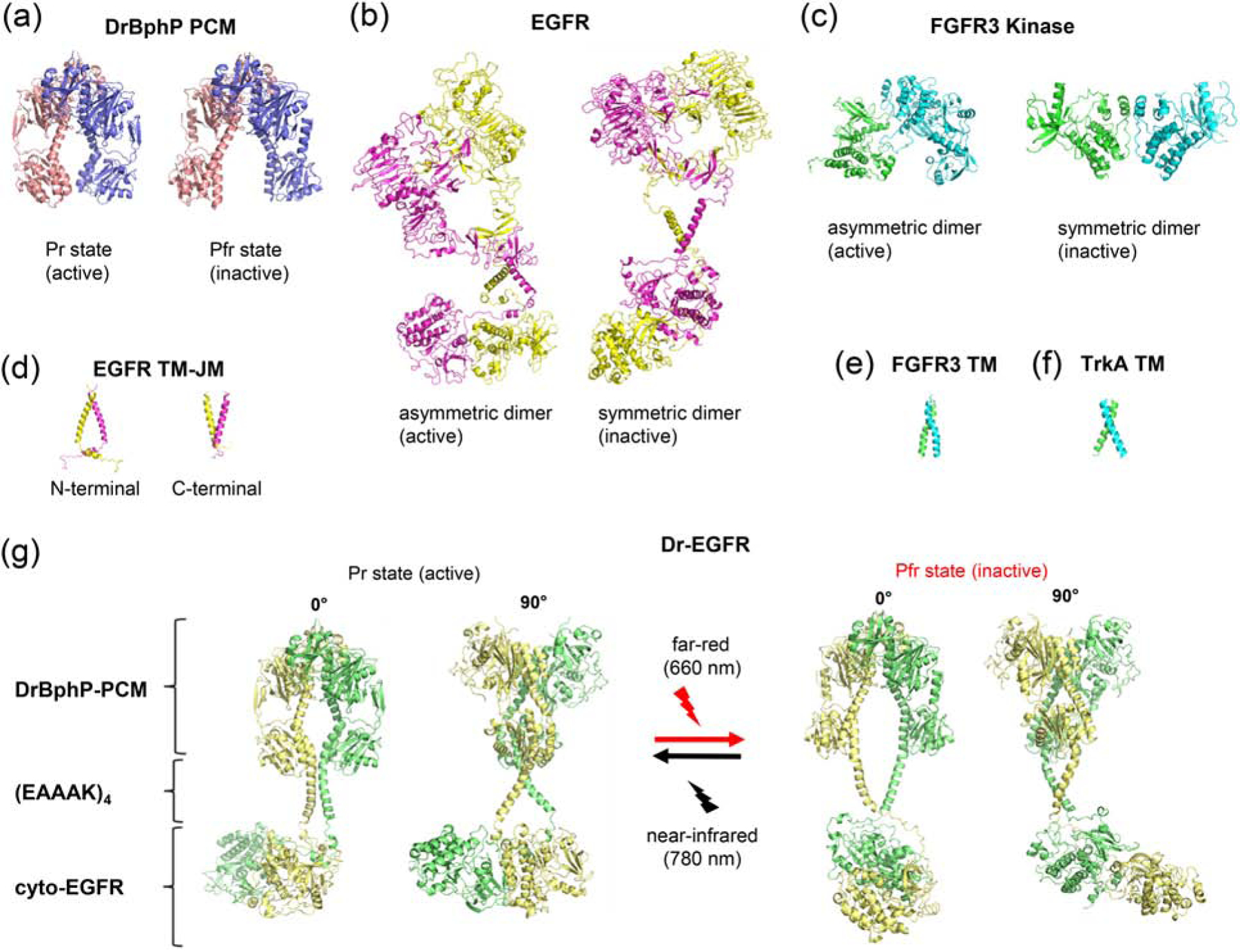
(a) X-ray structures of DrBphP-PCM in the active (Pr) (PDB 4O01) and inactive (Pfr) (PDB 4O0P) states [13]. (b) ab initio model of full-length EGFR [32] (c) X-ray structures of asymmetric (active) (PDB 3GQI [37]) and symmetric (inactive) (PDB 1FGK [35]) (d) NMR structures of transmembrane (TM) and juxtamembrane (JM) domains of EGFR in the active (PDB 2M20 [30]) and inactive (PDB 2M0B [30]) states. (e) NMR structure of TM of FGFR3 (PDB 2LZL [30]). (f) NMR structure of TM of TrkA (PDB 2N90 [36]). (g) Structural model of Dr-EGFR opto-RTK in its active (Pr) and inactive (Pfr) states composed of DrBphP-PCM, (EAAAK)4 and cytoplasmic EGFR JM and kinase domains.
