FIGURE 4.
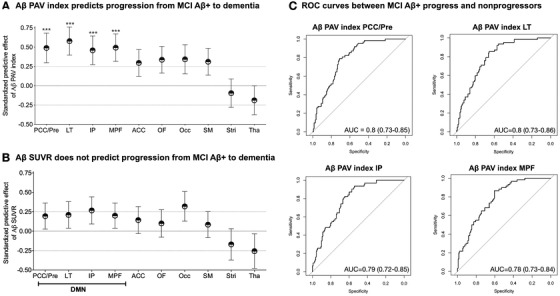
Amyloid beta (Aβ) percentage of abnormal voxels, rather than standardized uptake value ratio (SUVR) load, in brain's default mode network regions predicts the progression of Aβ positive mild cognitive impairment (MCI) individuals to dementia. The dots represent predictive effects (β estimates) of standardized baseline biomarkers (z‐scores) to progression to dementia using logistic regressions. The bars represent standard errors of β estimates. A, In Aβ positive MCI individuals, Aβ percentage of abnormal voxels (PAV) index in the posterior cingulate and precuneus (PCC/Pre), lateral temporal (LT), inferior parietal (IP), and medial prefrontal (MPF) predicted progression to dementia over 2 years. B, In Aβ positive MCI individuals, Aβ SUVR did not predict progression to dementia. C, Aβ PAV index accurately separated Aβ positive MCI (MCI Aβ+) progressors from non‐progressors. The models were adjusted for age, sex, years of formal education, apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 status, general cognitive performance at baseline (Mini‐Mental State Examination [MMSE] score), and Bonferroni corrected at P < .05. ACC, anterior cingulate; Occ, occipital; OF, orbitofrontal; SM, somatomotor; Stri, striatum; Tha, thalamus. *** P < .0001
