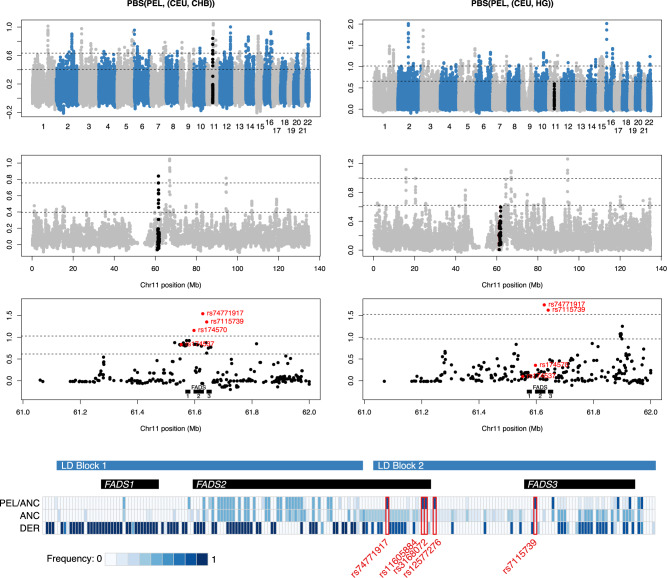
Fig. 2.
PBS on the Native American branch. Left column: PBS(PEL,(CEU, CHB)). Right column: PBS(PEL,(CEU, HG)). Upper row: genome-wide PBS in overlapping 20-SNP windows, shifted by 5 SNPs. Black points indicate the region Chr11:61-62Mb (hg19). Second row: chromosome 11 PBS in overlapping 20-SNP windows. Third row: per-SNP PBS in the region Chr11:61-62Mb. Horizontal lines indicate upper 0.01 and 0.001 genome-wide PBS quantiles. Red labeled points indicate SNPs previously identified as targets of selection (Fumagalli et al. 2015; Amorim et al. 2017). Top three rows restricted to 903,961 autosomal SNPs present on the 1,240k capture array with a minor allele frequency of at least 5% in at least one of the four populations. Fourth row: frequencies for all SNPs at >1% frequency in at least one population in CEU and CHB individuals carrying the derived haplotype (DER), the ancestral haplotype (ANC), and for PEL individuals carrying the ancestral haplotype (PEL/ANC). Color indicates the frequency of the variant that is rarer on the ancestral haplotype. Highlighted in red are five LD block 2 SNPs that have >50% difference in frequency between ANC and PEL/ANC, and at most 10% frequency in DER.