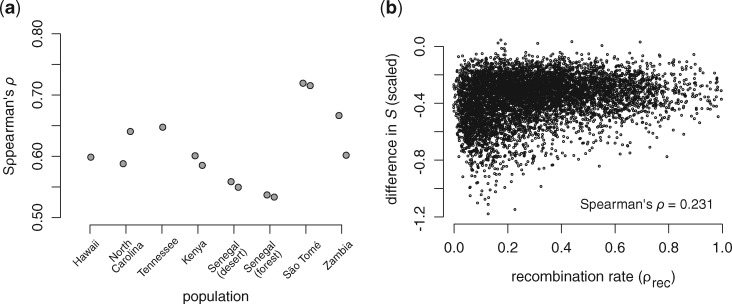
Fig. 3.
Correlations between genetic diversity (the number of segregating sites: S) and recombination rate across populations of Zaprionus indianus (a). Correlations did not systematically differ between populations in the invasive and native regions of the species’ range. However, the mean difference in diversity for a given genomic window was positively correlated with recombination rate (b). Populations with two points in (a) represent populations where we sampled more than four individuals and estimated S using two independent random subsamples of those individuals. In (b), the difference in S (mean in invasive populations−mean in native populations) was scaled by mean levels of diversity for a given recombination rate quantile.