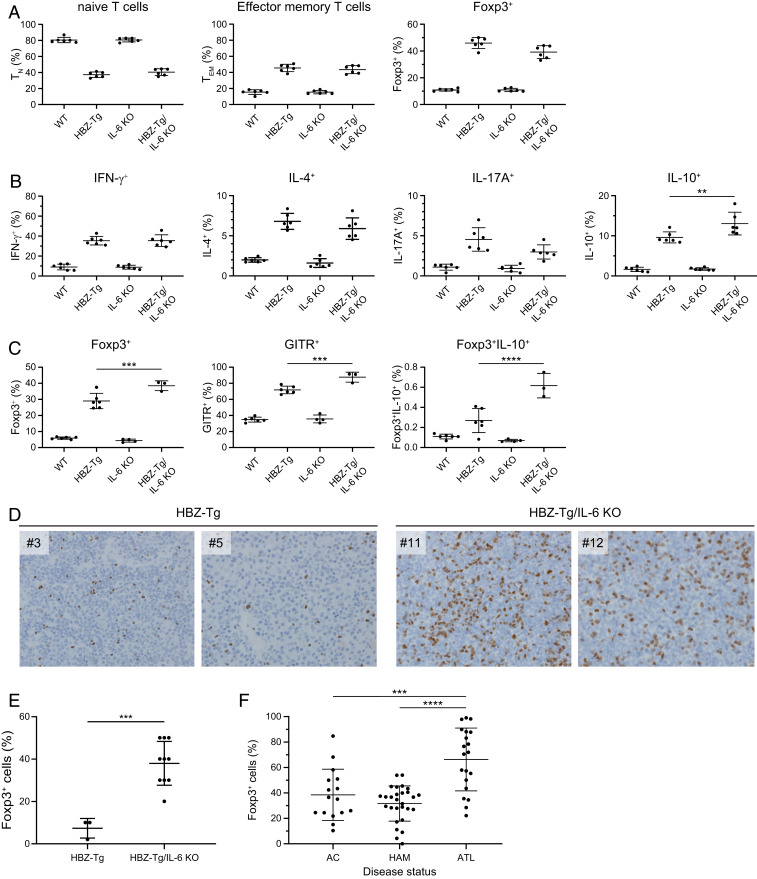
Fig. 2.
IL-10–producing CD4+ T cells are increased in HBZ-Tg/IL-6 KO mice. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of T cell subsets. Mouse splenocytes were collected from WT, HBZ-Tg, IL-6 KO, and HBZ-Tg/IL-6 KO mice at age 4 wk. Cells were stained with anti-CD4, anti-CD44, and anti-CD62L antibodies for naïve and effector memory T cells, and with anti-Foxp3. (B) Cytokine production by CD4+ T cells from 4-wk-old mice. Splenocytes were stimulated with PMA/ionomycin in the presence of protein transport inhibitor for 5 h and then stained with specific antibodies. (C) Expression of Treg-related molecules in CD4+ cells collected from 16-wk-old mice. Splenocytes were stimulated with PMA/ionomycin in the presence of protein transport inhibitor for 5 h and then stained with specific antibodies. (D) Immunohistochemical analysis for Foxp3 in lymph node and spleen of HBZ-Tg and HBZ-Tg/IL-6 KO mice (original magnification 40×). (E) Percentage of cells that are Foxp3+ in primary lymphomas of HBZ-Tg (n = 3) and HBZ-Tg/IL-6 KO (n = 10) mice. The data were obtained from immunohistochemical analysis. (F) Foxp3 expression in CD4+CADM1+ T cells from HTLV-1–infected subjects. AC, asymptomatic carrier (n = 16); HAM/TSP, HTLV-1–associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (n = 28); ATL, adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (n = 20).