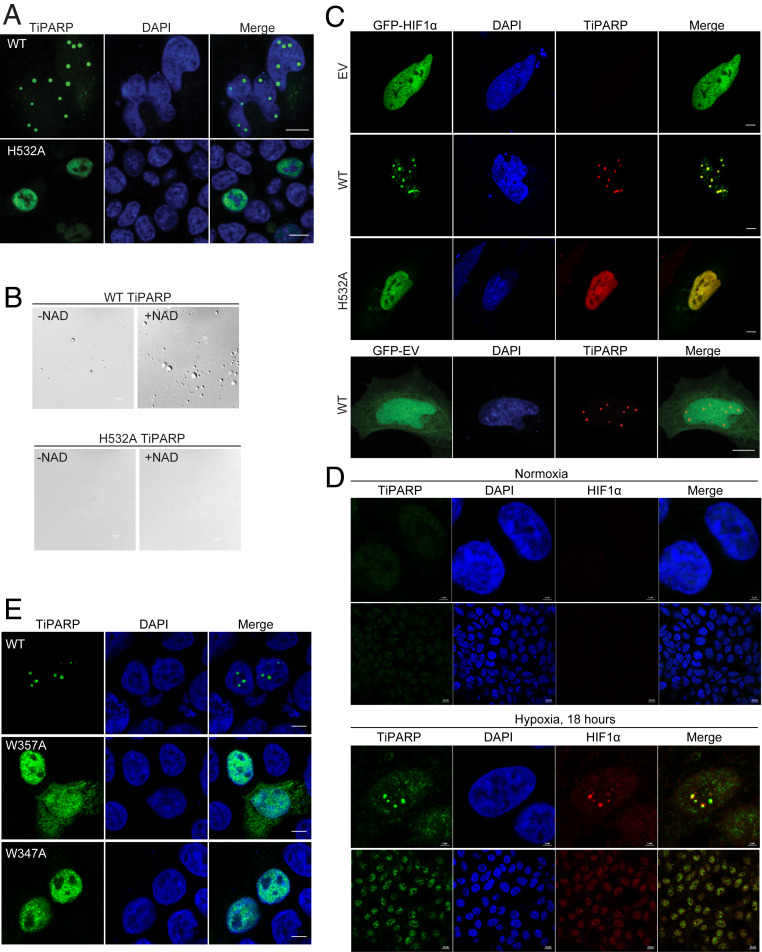
Fig. 3.
TiPARP forms nuclear foci and recruits HIF-1α. (A) HEK 293T cells were transfected with Flag-tagged WT and H532A mutant of TiPARP and analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy with anti-FLAG antibody (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (B) Purified Flag-tagged WT TiPARP, but not the H532A mutant, formed droplets in the presence of 100 μM NAD+. (Scale bar, 10 μm.) (C, Top) HEK 293T cells were cotransfected with GFP-HIF-1α, as well as empty vector (EV), Flag-tagged WT, or H532A mutant TiPARP. In the Bottom, as a negative control, cells were transfected with GFP empty vector and Flag-TiPARP. (Scale bar, 5 μm.) (D) HEK 293T cells were incubated in normal condition (normoxia) (Top section) or 1% O2 (hypoxia) (Bottom section) for 18 h, followed by fixation and immunofluorescent analysis using anti-TiPARP and anti-HIF1α antibodies. (Scale bar: 2 μm for zoomed images and 10 μm for unzoomed images.) Representative images are shown. (E) HEK 293T cells were transfected with Flag-tagged WT, W347A, or W357A mutant of TiPARP and analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy with anti-FLAG antibody (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). The images are representative of three independent experiments. (Scale bar, 5 μm.)