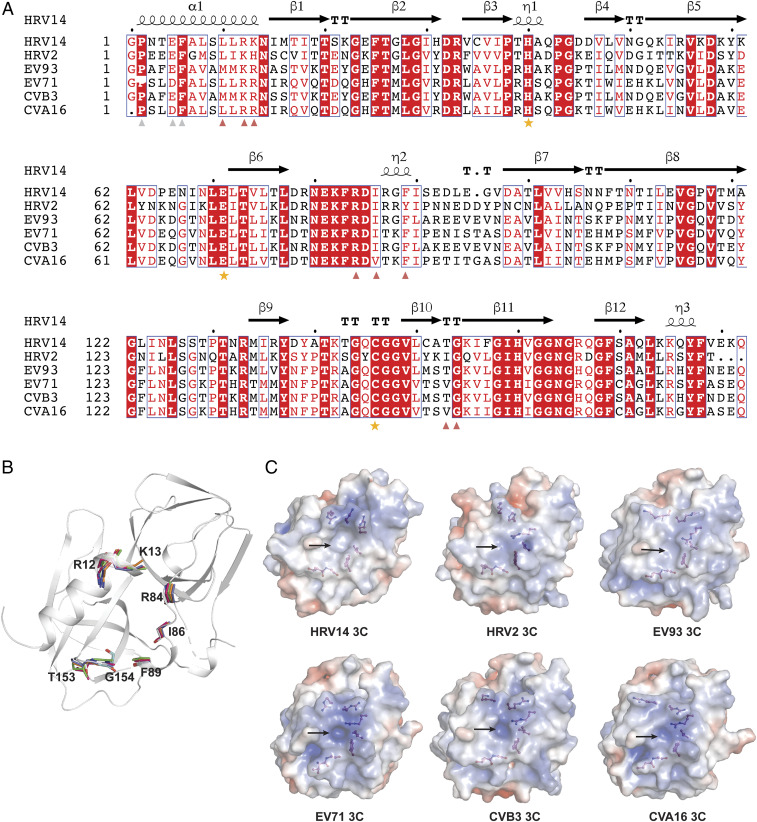
Fig. 5.
Key residues on 3C involved in both GGVV and genomic RNA interactions are conserved across a panel of enteroviruses. (A) Sequence alignment of HRV14 3C with its orthologs from HRV2, EV93, EV71, CVB3, and CVA16. The secondary structure of HRV14 3C is shown above the sequence and the three critical active-site residues are indicated with orange stars. Residues on HRV14 3C involved in both GGVV and 72-nt RNA binding are marked by red triangles, and residues involved in GGVV binding but not 72-nt RNA binding are marked by light gray triangles. (B) The structure of HRV14 3C (gray) is shown as a cartoon representation onto which its orthologs from HRV2 (PDB ID code 5FX5), EV93 (PDB ID code 3Q3X), EV71 (PDB ID code 3SJK), CVB3 (PDB ID code 2ZTZ), and CVA16 (PDB ID code 3SJ8) are superimposed. The backbone of the residues that are marked by red triangle in A are shown as stick models to highlight their structural conservation in space across HRV14 (gray), HRV2 (cyan), EV93 (orange), EV71 (green), CVB3 (blue), and CVA16 (hot pink). (C) The 3C proteases from HRV14, HRV2, EV93, EV71, CVB3, and CVA16 were rendered as an electrostatic surface representation (−5 to +5 kT/e), where hydrophobic surfaces are in whitish gray, basic in blue, and acidic in red. The residues marked by red triangle in A are shown as stick-and-ball models. Note that these residues are located around a similar pocket (marked with an arrow) on 3C in all six structures.